The
Cluster Subjects Across Study Sites
report is used to identify similar subjects. It t does so by constructing a cross domain data set using as much data as possible (subject to user options). Next, it calculates Euclidean distances to compute a
distance matrix
and performs
hierarchical clustering
of subjects, across all of the study centers. Findings values are averaged by
USUBJID
, test code, visit number, and time point (if available) if there are multiple measurements for a visit or time point. The goal of this exercise is to identify pairs of subjects with a very small distance. This could be an indication that these subjects are in fact the same individual who has enrolled at multiple sites.
Running this report using the
Nicardipine
sample setting and default options generates the output shown below. This report uses pre-dosing information with the goal of identifying subjects that have enrolled at two or more clinical sites.
The
Cluster Subjects Across Study Sites
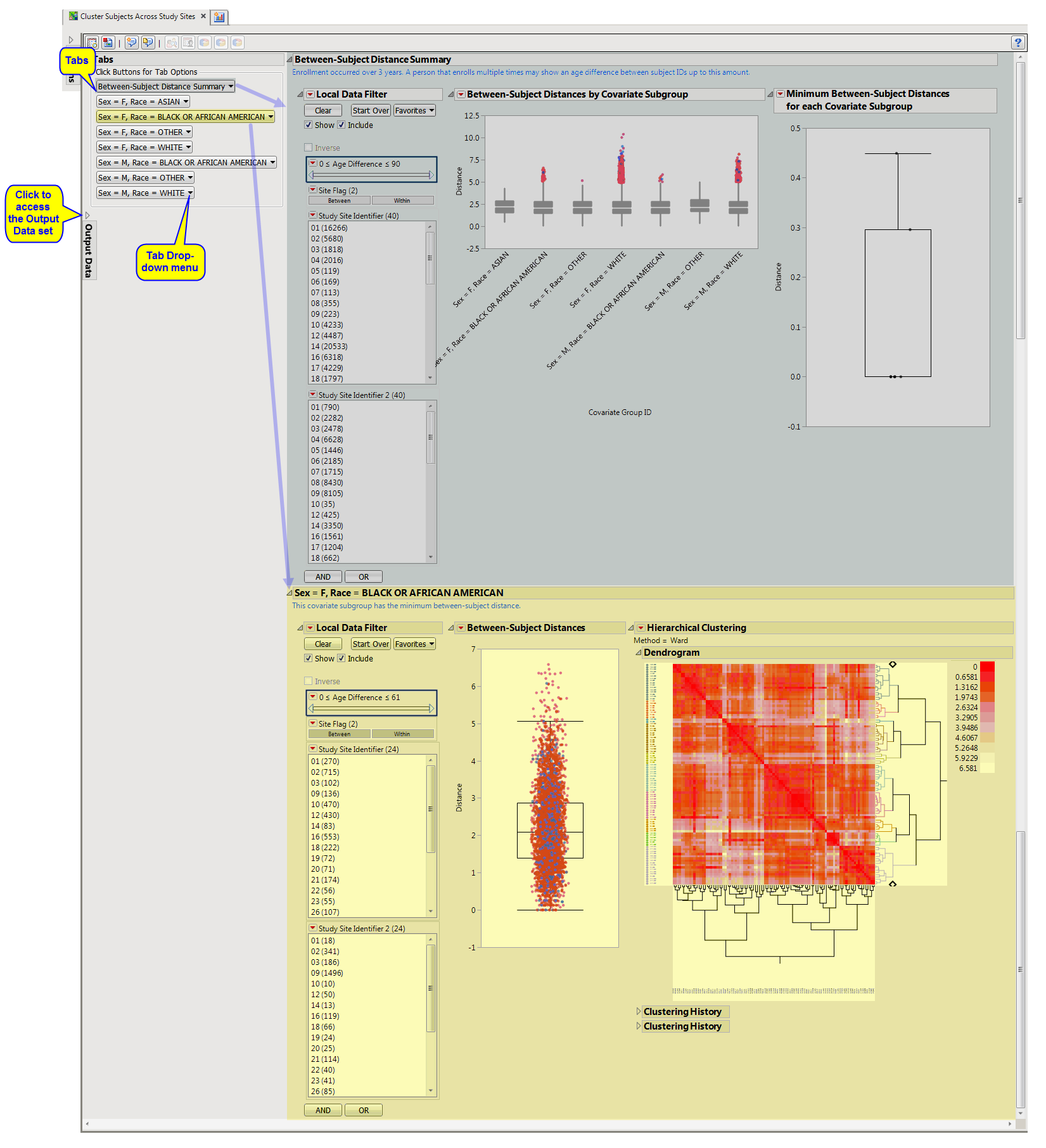
report shows the results of clustering of the subjects on the basis of different combinations of covariates (demographic groups in this example). The results for each grouping are presented on a separate “section”. report initially shows two sections
Between-Subject Distance Summary
and
Subgroup Clustering
. Use the available options in each section to drill-down into the data.
This pane enables you to access and view the output plots and associated data sets on each section. Use the drop-down menu to view the section in the
Results
pane or remove the section and its contents from the
Results
pane.
|
•
|
Box plots
are presented for all pairwise distances between subjects in the selected
population
. Pairs are limited based on selections from the
Cluster subjects matching these criteria
panel of the
dialog
.
|
|
•
|
One Box Plot of
Minimum Between-Subject Distances for Each Site
. The minimum distance from each
covariate
subgroup is presented in the box plot to the right.
|
The subgroup with the most similar pair of subjects is presented in the
Subgroup Clustering
section.
|
•
|
A
Local Data Filter
to subset histograms to data of interest is available.
|
In this example, data are filtered for a particular set of study monitors. Age (and height and weight, if available) are presented to limit pairs to those that are more likely to indicate a match between two subjects. Selecting
Within
subsets to pairs from subjects within the same site. Selecting
Between
subsets to subjects from different sites.
Refer to the
Data Filter
documentation for more information
One or more
Subgroup Clustering
sections: Only one section is opened initially. The name of this section is dependent on the covariate values used (as specified in the
Cluster subjects matching these criteria
panel) and the subgroup that is identified with the minimum pairwise distance. Other subgroup results can be opened from the
Results Sections
menu.
|
•
|
A
Box Plot
showing all pairwise distances between white females across all sites. Smaller distances indicate individuals that are more similar based on pre-dose information selected for use from the
dialog
. Using the data filter to subset to pairs with a small age, height and weight difference, we can highlight them in the
hierarchical clustering
profile or examine in the data table to assess similarity.
|
|
•
|
A
Dendrogram
showing the Hierarchical Clustering performed to identify subsets of subjects that might be very similar, for example, a subject that has attended at least 3 sites. Points indicating highly similar pairs of subjects can be selected from the
box plot
, and these rows can be highlighted in the clustering heat map.
|
|
•
|
A Local Data Filter to subset histograms to data of interest, for example, to data for a particular set of study monitors. Age (and height and weight, if available) are presented to limit pairs to those that are more likely to indicate a match between two subjects. Selecting
Within
subsets to pairs from subjects within the same site. Selecting
Between
subsets to subjects from different sites.
|
|
•
|
Profile Subjects
: Select subjects and click
|
|
•
|
Show Subjects
: Select subjects and click
|
|
•
|
Show Rows in Heat Map
: Select points that represent pairs of subjects in the
Box Plot
s
and click
|
|
•
|
Subset Clustering
: On a subgroup
clustering
page, subsets clustering to subjects, based on pairs selected from corresponding box plot.
|
|
•
|
Revert Clustering
: Click
|
|
•
|
Click
|
Output includes one summary data set (named
csass_sum_XXX
1
, by default) containing one record per subject with pre-dosing data, one data set of all pairwise distances within the
covariate
subgroups (named
csass_alldist_XXX
, by default), one data set containing minimum pairwise distances for each covariate subgroup (named
csass_mindist_XXX
), by default), one data set per covariate subgroup containing pairwise distances (named
csass_p_Y_XXX
, by default, where
Y
is indexed 1 to the number of covariate subgroups) and one data set per covariate subgroup containing the
distance matrix
of subjects within the covariate subgroup (named
csass_Y_XXX
, by default, where
Y
is indexed 1 to the number of covariate subgroups).
|
•
|
Click
|
|
•
|
Click
|
|
•
|
Click
|
|
•
|
Click the
arrow to reopen the completed report dialog used to generate this output.
|
|
•
|
Click the gray border to the left of the
Options
tab to open a dynamic report navigator that lists all of the reports in the review. Refer to
Report Navigator
for more information.
|
No testing is performed. Subjects are clustered within each site according to the selected clustering methodology. Refer to the JMP documentation on
hierarchical clustering
for statistical details.
Finally, you can restrict the analysis by subsetting the subjects using a variety of filters so that only those subjects meeting the specified conditions are included in the clustering. You can choose to include distinct populations of subjects. You can further restrict the analysis to those subjects that meet either a predefined or
de novo
unique set of specified conditions.
Remove all variables with missing values
,
Remove variables from analysis with a missing data percentage of at least:
The
_XXX
designation is used to designate a one- to three-digit number that is added sequentially to prevent overwriting of existing data sets.
Subject-specific filters must be created using the
Create Subject Filter
report prior to your analysis.
For more information about how to specify a filter using this option, see
The SAS WHERE Expression
.