Every flat map misrepresents the surface of the Earth in some way. Maps cannot match a globe in truly representing the surface of the entire Earth. A map projection is used to portray all or part of the round Earth on a flat surface. This cannot be done without some distortion. Every projection has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. A map can show one or more, but not all, of the following: true direction, distance, area, or shape. JMP uses a couple of projections (Albers Equal Area Conic and Kavrayskiy VII) for its maps. Within Images, you can select from two built-in map images, or you can connect to a Web Map Service to retrieve a background image.
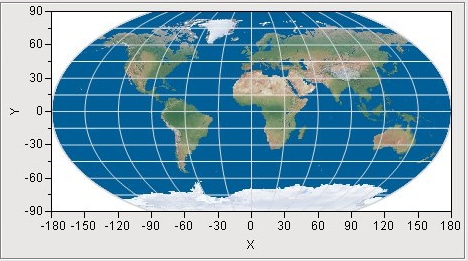
Simple Earth and Detailed Earth both support a geodesic scaling. In Figure 15.13, the Earth appears as a rectangle, where the width is twice as wide as the height. If we were to take this rectangle and roll it up, we would have a cylinder. In reality, we know that the Earth does not form a cylinder, but rather a sphere. You can use a geodesic scaling, which transforms the map to a more realistic representation of the Earth. To use the geodesic scaling, change the type of scale on the axes.
To change the axes scale:
|
1.
|
Right-click the X or Y axis and then select Axis Settings.
|
|
2.
|
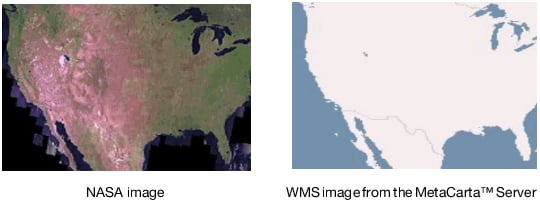
To locate a server, launch the add-in through the menu items Add-Ins > Map Images > WMS Explorer. The add-in presents a text box for entering the url of a known WMS server. Alternatively, you can make a selection from a drop-down list of pre-discovered WMS servers (the list can be out of date). After specifying a WMS server, select Get Layers. Using Get Layers is not necessary if selecting from the drop-down list or if clicking Enter after entering a URL. This sends a request to the WMS server for a list of layers that the server supports. The returned list appears in the list box on the left, labeled Layers. A map of the world appears as an outline in the graph to the right. Selecting a layer makes a request to the WMS server to return a map, using the specified layer, that represents the entire earth. Selecting a different layer generates a different map.
The graph is a typical graph in JMP, which means that all the regular JMP controls are available to you. You can adjust the axes or use the zoom tool (found on the hidden menu bar) just as you would in JMP. You can also right-mouse-click to select Size/Scale > Size to Isometric to return the graph to a proper aspect ratio. You can also select Background Map, where you can adjust the boundary map.