Response Screening Report Tables
The default tables included in the Response Screening report window depend on the selections made in the launch window. The Result Table is always shown and the 2 by M Results table is shown for two level categorical responses with one or more categorical predictors.
Result Table
The Result Table in the Response Screening report contains a row for each pair of Y and X variables. The columns of the table contain measures and model fit statistics that are specific to the selected fit and Y and X modeling types.
Group
(Appears only if there is a grouping variable.) The level of the grouping column.
Y
The specified response columns.
X
The specified factor columns.
Count
The number of rows used for testing, or the corresponding sum of the Freq or Weight variable.
PValue
The p-value for the significance test corresponding to the pair of Y and X variables. For more information about Fit Y by X statistics, see “Introduction to Fit Y by X” in Basic Analysis.
Logworth
The quantity -log10(p-value). This transformation adjusts p-values to provide an appropriate scale for graphing. A value that exceeds 2 is significant at the 0.01 level (-log10(0.01) = 2).
FDR PValue
The False Discovery Rate p-value calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg technique. This technique adjusts the p-values to control the false discovery rate for multiple tests. If there is no Group variable, the set of multiple tests includes all tests displayed in the table. If there is a Group variable, the set of multiple tests consists of all tests conducted for each level of the Group variable. For more information about the FDR correction, see Benjamini and Hochberg (1995). For more information about the false discovery rate, see Statistical Details for the Response Screening Platform.
FDR Logworth
The quantity -log10(FDR PValue). This is the statistic used for plotting and assessing significance. Note that small p-values result in high FDR logworth values. Cells corresponding to FDR logworth values greater than two (p-values less than 0.01) are colored with an intensity gradient.
Effect Size
Indicates the extent to which response values differ across the levels or values of X. Effect sizes are scale invariant.
– When Y is continuous, the effect size is the square root of the average sum of squares from the hypothesis test divided by a robust estimate of the response standard deviation. If the interquartile range (IQR) is nonzero and IQR > range/20, the standard deviation estimate is IQR/1.3489795. Otherwise, the sample standard deviation is used.
– When Y is categorical and X is continuous, the effect size is the square root of the average ChiSquare value for the whole model test.
– When Y and X are both categorical, the effect size is the square root of the average Pearson ChiSquare value.
Rank Fraction
The rank of the FDR Logworth expressed as a fraction of the number of tests. If the number of tests is m, the largest FDR Logworth value has Rank Fraction 1/m, and the smallest has Rank Fraction 1. The Rank Fraction is used in plotting the PValues and FDR PValues in rank order of decreasing significance.
RSquare
(Appears only when Y is continuous.) The coefficient of determination, which measures the proportion of total variation explained by the model.
Slope
(Appears only if the Logworth by Slope plot is shown in the report window.) The slope of the simple linear regression model that relates the corresponding pair of Y and X variables.
Kappa
(Appears only when specified in the launch window. Available only for categorical Y and X with the same number of levels.) A measure of agreement between Y and X.
Corr
(Appears only when specified in the launch window.) The Pearson product-moment correlation. For categorical variables, the correlation is calculated in terms of the indices defined by the value ordering.
The following columns are added to the Result Table when the Robust option is selected in the launch window. The Robust option applies only when Y is continuous, so Robust column cells are empty when Y is categorical.
Robust PValue
The p-value for the significance test corresponding to the pair of Y and X variables using a robust fit.
Robust Logworth
The quantity -log10(Robust PValue).
Robust FDR PValue
The False Discovery Rate calculated for the Robust PValues using the Benjamini-Hochberg technique. If there is no Group variable, the multiple test adjustment applies to all tests displayed in the table. If there is a Group variable, the multiple test adjustment applies to all tests conducted for each level of the Group variable.
Robust FDR Logworth
The quantity -log10(Robust FDR PValue).
Robust Rank Fraction
The rank of the Robust FDR Logworth expressed as a fraction of the number of tests.
Robust Chisq
The chi-square value associated with the robust test.
Robust Sigma
The robust estimate of the error standard deviation.
Robust Outlier Portion
The portion of the values whose distance from the robust mean exceeds three times the Robust Sigma.
The following columns are added to the Result Table when the Cauchy option is selected in the launch window. The Cauchy option applies only when Y is continuous, so Cauchy column cells are empty when Y is categorical.
Cauchy PValue
The p-value for the significance test corresponding to the pair of Y and X variables using a Cauchy fit.
Cauchy Logworth
The quantity -log10(Cauchy PValue).
Cauchy FDR PValue
The False Discovery Rate calculated for the Cauchy PValues using the Benjamini-Hochberg technique. If there is no Group variable, the multiple test adjustment applies to all tests displayed in the table. If there is a Group variable, the multiple test adjustment applies to all tests conducted for each level of the Group variable.
Cauchy FDR Logworth
The quantity -log10(Cauchy FDR PValue).
Cauchy Rank Fraction
The rank of the Cauchy FDR Logworth expressed as a fraction of the number of tests.
Cauchy ChiSquare
The chi-square value associated with the test from the Cauchy fit.
Cauchy Sigma
The estimate of the error standard deviation from the Cauchy fit.
Cauchy Outlier Portion
The portion of the values whose distance from the mean of the Cauchy fit exceeds three times the Cauchy Sigma.
2 by M Results
The 2 by M table contains results that you can use to investigate the relationship between a two level categorical response and a categorical predictor. For each response and predictor pair, the relative risk, risk difference, and odds ratio are reported by default. A column of confidence interval plots is also shown for each statistic with a dashed line at 1 for relative risk and odds ratios, and at 0 for the risk difference. This dashed line represents no difference between response categories due to the predictor level. A red confidence interval indicates a statistically significant difference in response levels due to the predictor level while a blue confidence interval indicates no significant difference. Right-click on the table and select Columns to add counts, confidence intervals, labels, or the FDR Logworth values to the table. The first level is set as the baseline and each of the other levels is compared to it.
Note: The 2 by M Results report is available only when there are one or more two level categorical responses with one or more categorical predictors.
Means Differences
Each row in the Means Differences table compares a response across two levels of a categorical factor. Use the Means Comparisons option in the launch window to specify whether to compare each level to a control level or to compare all possible level combinations. The table indicates the X variables and the levels that are compared.
The Difference column in the Means Differences table contains the estimated difference in the response means across the two levels. If the Robust option is selected, robust estimates of the means are used. There are also columns for the FDR p-value and the FDR logworth, which are obtained from testing whether or not the difference between the two means is zero. Right-click on the table and select Columns to add confidence intervals or unadjusted statistics to the table.
There is a column of plots of overlaid unadjusted confidence intervals and Benjamini-Yekutieli FDR adjusted confidence intervals for the Difference value. The Difference value is marked by a red or blue circle and the two confidence intervals extend from each circle. A red circle indicates that one or both of the confidence intervals does not contain zero. A blue circle indicates that both of the confidence intervals contain zero. The inner confidence interval represents the unadjusted confidence interval and the outer confidence interval represents the B-Y FDR adjusted confidence interval.
The quantile for the B-Y FDR adjusted confidence limits is calculated as follows:
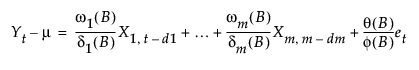
where R is the number of FDR significant tests at the α level among a total of m tests. By default, α = 0.05 and 95% confidence limits are created. See Benjamini (2005).
Note: The Means Differences table is available only when there is one or more continuous responses and one or more categorical predictors.