Statistical Details for Short Run Control Charts
This section describes how control limits for Short Run control charts are calculated in Control Chart Builder. See Wise and Fair (2006).
Statistical Details for Product Statistics
The Product Statistics table gives the target and sigma values for each product. The product target, Tj, is the estimated mean value of the observations in product j. The product sigma, σj, is the estimated standard deviation for each product. The product target and product sigma values are calculated using the following formulas.
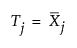
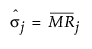
If a subgroup is specified, the product sigma is calculated using the following formula:
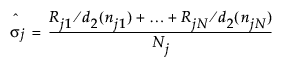
If a subgroup is specified and there are unequal subgroup sizes, an overall unadjusted sigma is calculated using the following formula:
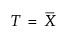
If no Product/Part variable is specified, the overall mean and estimated standard deviation are shown in the table and are calculated using the following formulas:
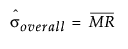
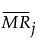
where:
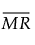 = the mean of the nonmissing moving ranges for product j
= the mean of the nonmissing moving ranges for product j
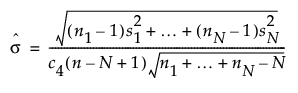 = the mean of the nonmissing moving ranges
= the mean of the nonmissing moving ranges
d2(n) = expected value of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation.
nji = sample size of ith subgroup for part j
Rji = the range of ith subgroup for part j
Nj is the number of subgroups in part j for which nij ≥ 2
Ri = the range of ith subgroup
N is the number of subgroups for which ni ≥ 2.
The target and sigma values are used to calculate the points on the Short Run control charts. For centered charts, each observation is centered by subtracting off the Target value for the corresponding product. For standardized charts, each observation is standardized by subtracting off the Target value for the corresponding product and dividing by the product Sigma value.
Statistical Details for Short Run Difference and Moving Range on Centered Charts
Control limits for Short Run Difference charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run Difference chart = 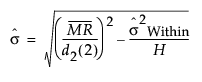
CL for Short Run Difference chart = 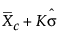
UCL for Short Run Difference chart = 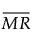
Control limits for Short Run Moving Range on Centered charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run MR on Centered chart = 0
CL for Short Run MR on Centered chart = 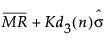
UCL for Short Run MR on Centered chart = 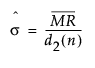
The standard deviation for Short Run Difference and Moving Range on Centered charts is estimated as follows:
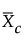
where:
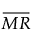 = the mean of the centered measurements
= the mean of the centered measurements
K = the sigma multiplier and is set to 3 by default
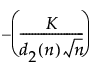 = the mean of the nonmissing moving ranges
= the mean of the nonmissing moving ranges
d2(n) = expected value of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation
d3(n) = standard deviation of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation.
Note: Moving Range charts in Control Chart Builder use a range span of n = 2.
Statistical Details for Short Run Z and Moving Range on Standardized Charts
Control limits for Short Run Z charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run Z chart = 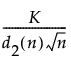
CL for Short Run Z chart = 0
UCL for Short Run Z chart = 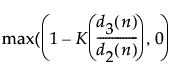
Control limits for Short Run Moving Range on Standardized charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run MR on Standardized chart = 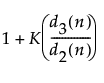
CL for Short Run MR on Standardized chart = 1
UCL for Short Run MR on Standardized chart = 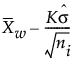
where:
K = the sigma multiplier and is set to 3 by default
d2(n) = expected value of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation
d3(n) = standard deviation of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation.
Note: Moving Range charts in Control Chart Builder use a range span of n = 2.
The centerline for the Short Run Z chart is 0 and the centerline for the Short Run Moving Range chart on standardized data is 1.
Statistical Details for Short Run Average Difference and Range on Centered Charts
Control limits for Short Run Average Difference charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run Average Difference chart = 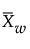
CL for Short Run Average Difference chart = 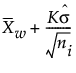
LCL for Short Run Average Difference chart = 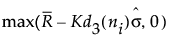
Control limits for Short Run Range on Centered charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run R on Centered chart = 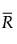
CL for Short Run R on Centered chart = 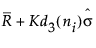
UCL for Short Run R on Centered chart = 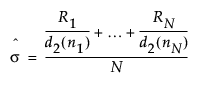
The standard deviation for Short Run Difference and Range on Centered charts is estimated as follows:
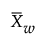
where:
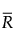 = weighted average of subgroup differences
= weighted average of subgroup differences
K = the sigma multiplier and is set to 3 by default
ni = sample size of ith subgroup
d2(n) is the expected value of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation
d3(n) is the standard deviation of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation
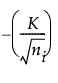 = the mean of the nonmissing ranges
= the mean of the nonmissing ranges
Ri is the range of ith subgroup
N is the number of subgroups for which ni ≥ 2.
Statistical Details for Short Run Z and Range on Standardized Charts
Control limits for Short Run Z charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run Z chart = 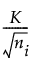
CL for Short Run Z chart = 0
UCL for Short Run Z chart = 
Control limits for Short Run Range on Standardized charts are computed as follows:
LCL for Short Run R on Standardized chart = D3
CL for Short Run R on Standardized chart = 1
UCL for Short Run R on Standardized chart = 
where:
K = the sigma multiplier and is set to 3 by default
ni = sample size of ith subgroup
d2(n) is the expected value of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation
d3(n) is the standard deviation of the range of n independent normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation.