 The Model Comparison Report
The Model Comparison Report
The initial Model Comparison report contains a Predictors report and a Measures of Fit report. The Predictors report shows all responses and all models being compared for each response. The fitting platform that created the predictor column is also listed. The Measures of Fit report shows measures of fit for each model. The columns are different for continuous and categorical responses.
Measures of Fit for Continuous Responses
RSquare
The r-squared statistic. In data tables that contain no missing values, the r-squared statistics in the Model Comparison report and original models match. However, if there are any missing values, the r-squared statistics differ.
RASE
The square root of the mean squared prediction error. This is computed as follows:
– Square and sum the prediction errors (differences between the actual responses and the predicted responses) to obtain the SSE.
– Denote the number of observations by n.
– RASE is:
RASE = 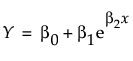
AAE
The average absolute error.
Freq
The column that contains frequency counts for each row.
Measures of Fit for Categorical Responses
Entropy RSquare
One minus the ratio of the negative log-likelihoods from the fitted model and the constant probability model. It ranges from 0 to 1.
Generalized RSquare
A measure that can be applied to general regression models. It is based on the likelihood function L and is scaled to have a maximum value of 1. The value is 1 for a perfect model, and 0 for a model no better than a constant model. The Generalized RSquare measure simplifies to the traditional RSquare for continuous normal responses in the standard least squares setting. Generalized RSquare is also known as the Nagelkerke or Craig and Uhler R2, which is a normalized version of Cox and Snell’s pseudo R2. See Nagelkerke (1991).
Mean -Log p
The average of -log(p), where p is the fitted probability associated with the event that occurred.
RASE
The root average squared prediction error. For categorical responses, the differences are between 1 and p, the fitted probability for the response level that actually occurred.
Mean Abs Dev
The average of the absolute values of the differences between the response and the predicted response. For categorical responses, the differences are between 1 and p (the fitted probability for the response level that actually occurred).
Misclassification Rate
The rate for which the response category with the highest fitted probability is not the observed category.
N
The number of observations.
“Training and Validation Measures of Fit” provides more information about measures of fit for categorical responses.