Example of Hierarchical Clustering
In this example, you group together countries by their 2009 crude birth and death rates per 1,000 people in order to examine clusters in the data.
1. Select Help > Sample Data Folder and open Birth Death Subset.jmp
2. Select Analyze > Clustering > Hierarchical Cluster.
3. Select birth and death and click Y, Columns.
4. Select country and click Label.
This selection ensures that the country column, rather than the row number, is used to label the dendrogram that appears when you click OK.
5. Click OK.
6. Click the Hierarchical Clustering red triangle and select Color Clusters.
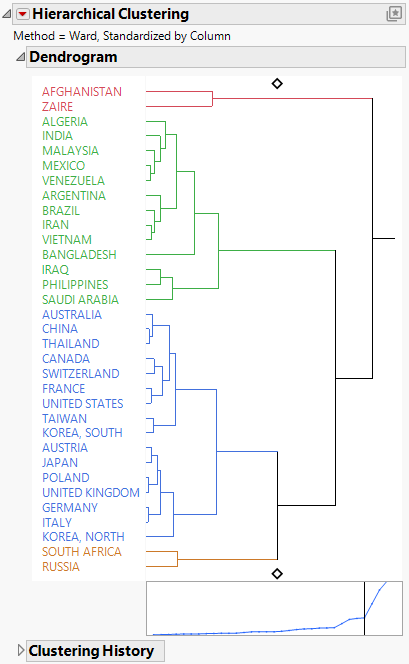
Figure 13.2 Hierarchical Clustering Report
The dendrogram shows how the clustering is conducted. The clustering process can be viewed by reading the dendrogram from left to right. Each step consists of combining the two closest clusters into a single cluster.
In the dendrogram, the relative distances between clusters are given by the horizontal distances between vertical lines that join the clusters. For example, Afghanistan and Zaire differ more than Malaysia differs from the cluster consisting of Mexico and Venezuela.
The diamonds are set at four clusters. The two clusters that are most recently joined to form the four cluster model are the cluster consisting of Algeria to Bangladesh and the cluster consisting of Iraq to Saudi Arabia. The distance between these two clusters is the point on the distance plot indicated by the vertical line when the diamond is set to 4. The distance is given in the Clustering History report next to Number of Clusters equal to 4. There, it is shown that the distance is 1.618708760 and that clusters beginning with Algeria and Iraq are combined to yield four clusters.
The distance graph has a noticeable change in slope at four clusters. The change in slope indicates that the differences in clusters that are joined up to the point where four clusters remain, are comparatively small. This suggests that four is a good choice for the number of clusters. Note that this is the number of clusters that was shown by default.
7. Click the Hierarchical Clustering red triangle and select Constellation Plot.
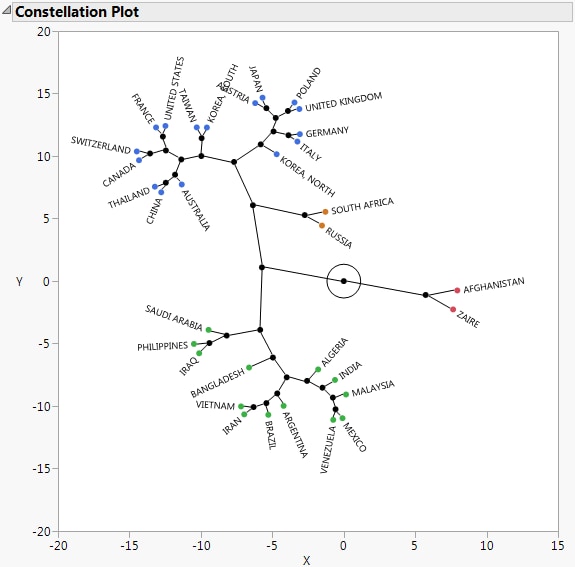
Figure 13.3 Constellation Plot
This constellation plot arranges the countries as endpoints and each cluster join as a new point. The lines represent membership in a cluster. The length of a line between cluster joins approximates the distance between the clusters that were joined. The constellation plot indicates that the cluster that contains Afghanistan and Zaire is about the same distance from each of the two primary clusters.