Passing-Bablok Fit Report
In the Bivariate platform, use the Fit Passing Bablok option to fit a regression model using the Passing-Bablok method. Passing-Bablok regression was developed for comparing measurements from two different analytical methods. The method assumes a linear relationship between the two variables with strong correlation. A line of fit and a dotted line for Y = X are added to the scatterplot. Use the Bland Altman Analysis option in the Passing-Bablok Fit red triangle menu to perform a paired t-test and Bland-Altman analysis.
The Passing-Bablok Fit report contains three tables.
Nonparametric: Kendall’s τ
Use Kendall’s τ to assess the correlation between the X and Y variables.
X
The X variable.
Y
The Y variable.
Kendall’s t
A nonparametric measure of correlation between the X and Y variables. Values are between -1 and 1 with a value near 0 indicating independence between the X and Y variables.
Prob>|τ|
The p-value associated with the hypothesis test of independence between the X and Y variables. A small p-value supports that the variables are dependent and that the Passing-Bablok method is appropriate.
CUSUM Test of Linearity
The CUSUM Test of Linearity table contains the results of a test for linearity. A small p-value would lead one to reject the null hypothesis of linearity, indicating that Passing-Bablok regression might not be appropriate.
Max CUSUM
The maximum of the absolute values of the cumulative sums of the values 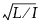 and
and 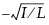 that are assigned to each row based on the sign of the residual and sorted by the perpendicular distance of each point to the Passing-Bablok line. I is the number of observations with a positive residual, and L is the number of observations with a negative residual. When there is strong correlation between methods, I is equal to L. Therefore, the cumulative sums are often sums of +1 and -1. A small CUSUM value indicates a random distribution of points on either side of the Passing-Bablok Line; this result supports the hypothesis of linearity.
that are assigned to each row based on the sign of the residual and sorted by the perpendicular distance of each point to the Passing-Bablok line. I is the number of observations with a positive residual, and L is the number of observations with a negative residual. When there is strong correlation between methods, I is equal to L. Therefore, the cumulative sums are often sums of +1 and -1. A small CUSUM value indicates a random distribution of points on either side of the Passing-Bablok Line; this result supports the hypothesis of linearity.
H
The test statistic for the CUSUM test. This test statistic is defined as the Max CUSUM divided by the square root of the number of negative residuals plus 1. This test statistic has a Kolmogorov-Smirnov distribution.
Prob > H
The p-value for the CUSUM test. Small p-values indicate that the Passing-Bablok procedure might not be appropriate.
Parameter Estimates
The Parameter Estimates table contains the Passing-Bablok fit estimates of the intercept and slope with corresponding 95% confidence intervals.
Matched Pairs Report
Use the Bland Altman Analysis option in the Passing-Bablok Fit red triangle menu to perform a paired t-test and Bland-Altman analysis. For more information about matched pairs, see Matched Pairs Analysis in Predictive and Specialized Modeling.
Bland-Altman Analysis
The Bland-Altman Analysis table contains the value, the standard deviation, and the confidence limits for the following parameters:
Bias
The mean difference between the X and Y variables.
Limits of Agreement
The upper and lower limits of agreement, which are set at bias ± z1-α/2*(standard deviation of the bias).