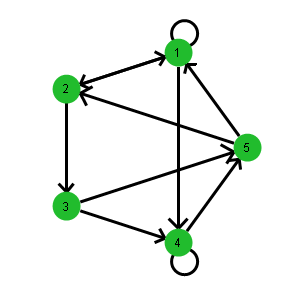
This is a two-level associative array. The associative array g contains five associative arrays (1, 2, 3, 4, and 5). In the containing array g, both the keys (1-5) and the values (the arrays that define the map) are important. In the inner associative arrays, the values do not matter. Only the keys are important.
dfs = Function( {ref, node, visited},
chnode = tmp << first;
visited = Recurse( ref, chnode, visited )
chnode = tmp << Next( chnode );
New Window( "Directed Graph",
edge = edges << Next( edge ),
{from, to} = Eval List(