Importing HDF5 Files
TASSEL is a software widely used in the plant genetics community. This software inputs and outputs a variety of file formats. We’ve already discussed importing the Importing GBS Files (.hmp and hapdip.hmp). The HDF5 file format differs from those in that the data for genotypes calls, genotype depth reads, and metadata for both SNPs and TAXA (samples) is contained in a binary-coded file instead of in a text file.
The HDF5 file is composed of thousands of individual files organized into a directory-like structure with numerous subdirectories. These include:
| • | The /Genotypes/…/Calls subdirectory contains as many files as there are samples. There can be from couple hundreds of files to many thousands. These files must be merged into a single data table. These files store the genotype data in binary format and must be recoded upon import. |
| • | Metadata related to the SNPs are found in both the /Positions/ and /Genotypes/_Descriptors/ subdirectories and must be joined into a second table. |
| • | The metadata related to the Taxa (samples) are found in both the /Taxa/ and /Genotypes/_Descriptors/ subdirectories and must be joined into a third table. |
| • | Information regarding Allele Frequency Order and Allele Counts from files in the /Genotypes/_Descriptors/ subdirectories are used to generate two additional tables. |
JMP Pro automatically generates the appropriate tables. In the end, there may be 4 tables depending on the sets of files you choose to import.
Importing HDF5 binary files
In this example, we import the ch01-g2f_2017_ZeaGBSv27_Imputed_AGPv4.h5 file.
• Select File > Open. An Open Data File window opens to the last location used.
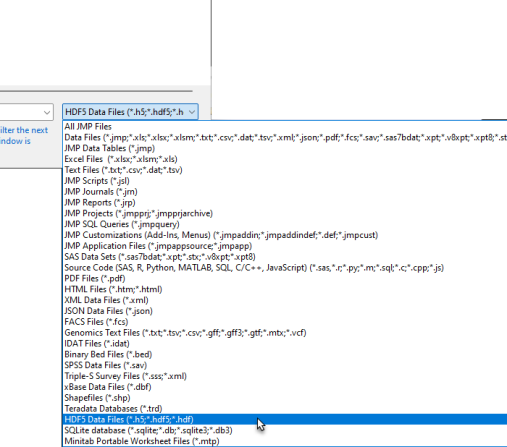
| 8 | Navigate to the location of the HDF5 file and use the drop-down menu (shown below) to select HDF5 Files (*.h5; *.hdf5; *.hdf). |
| 8 | Select the desired file. |
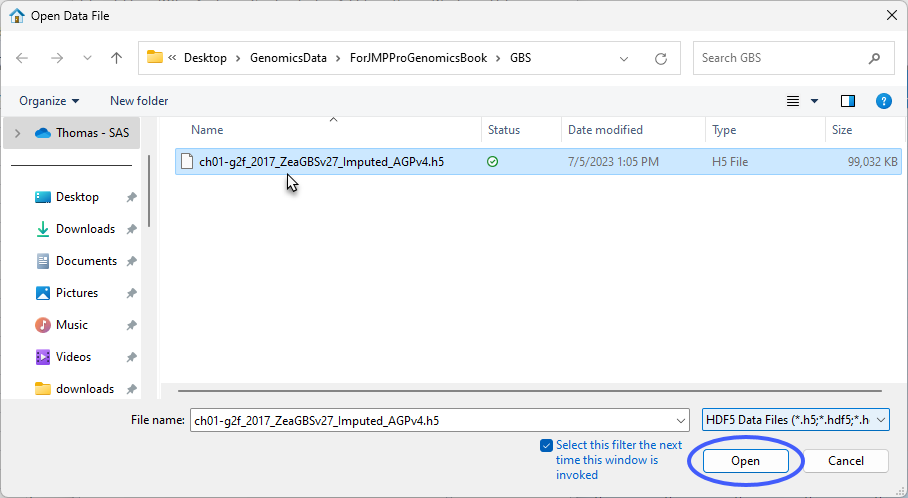
| 8 | Click Open. |
The Import HDF5 Tables window opens.
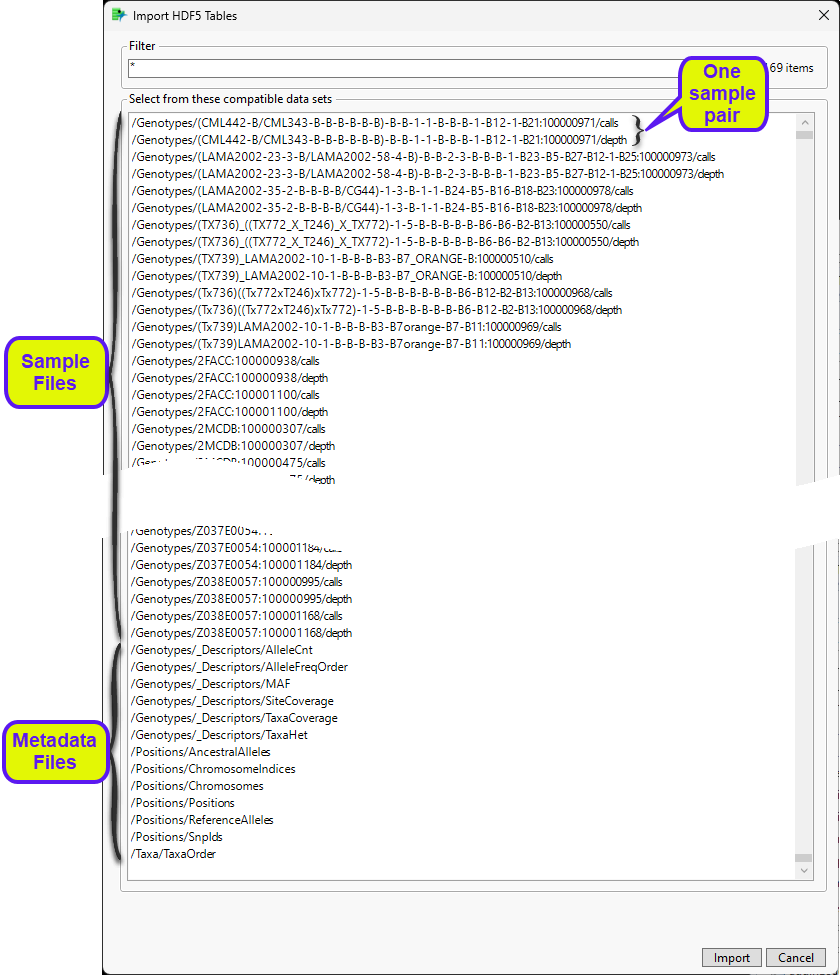
There are 3169 individual files in this data set. The 3154 sample files include 1577 calls files and an equal number of depth files. Each calls file, which contains the genotypes calls for an individual sample, has a corresponding depth file, which contains the results of each individual sequencing run for that sample. The thirteen metadate files contain a variety of annotation and other information about the samples and the markers. Not all these files (the depth files, for example) are to be imported.
As described above, we must import the data into separate files. The first set to be imported are the calls files.
The Import HDF5 Files window enables you to specify just the files to be imported. You could just hold down the CTRL key and select each calls file to be imported, for example, but that would be tedious, and you might miss a file or two. A better way to select the files is to use the filter option.
Enter **/calls in the Filter text box and click Return.
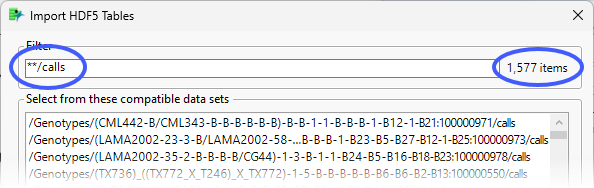
Applying the filter reduces the displayed files to just those ending in “calls”.
| 8 | Select all the /calls files and click . |
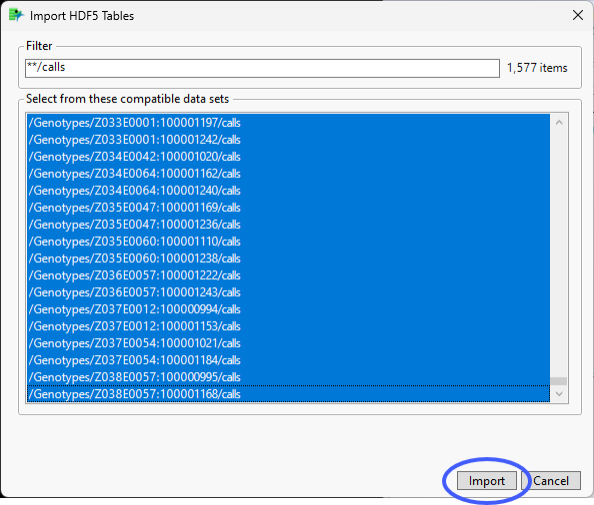
The files are imported and combined into the single Genotypes_Calls_Wide.jmp wide data table.
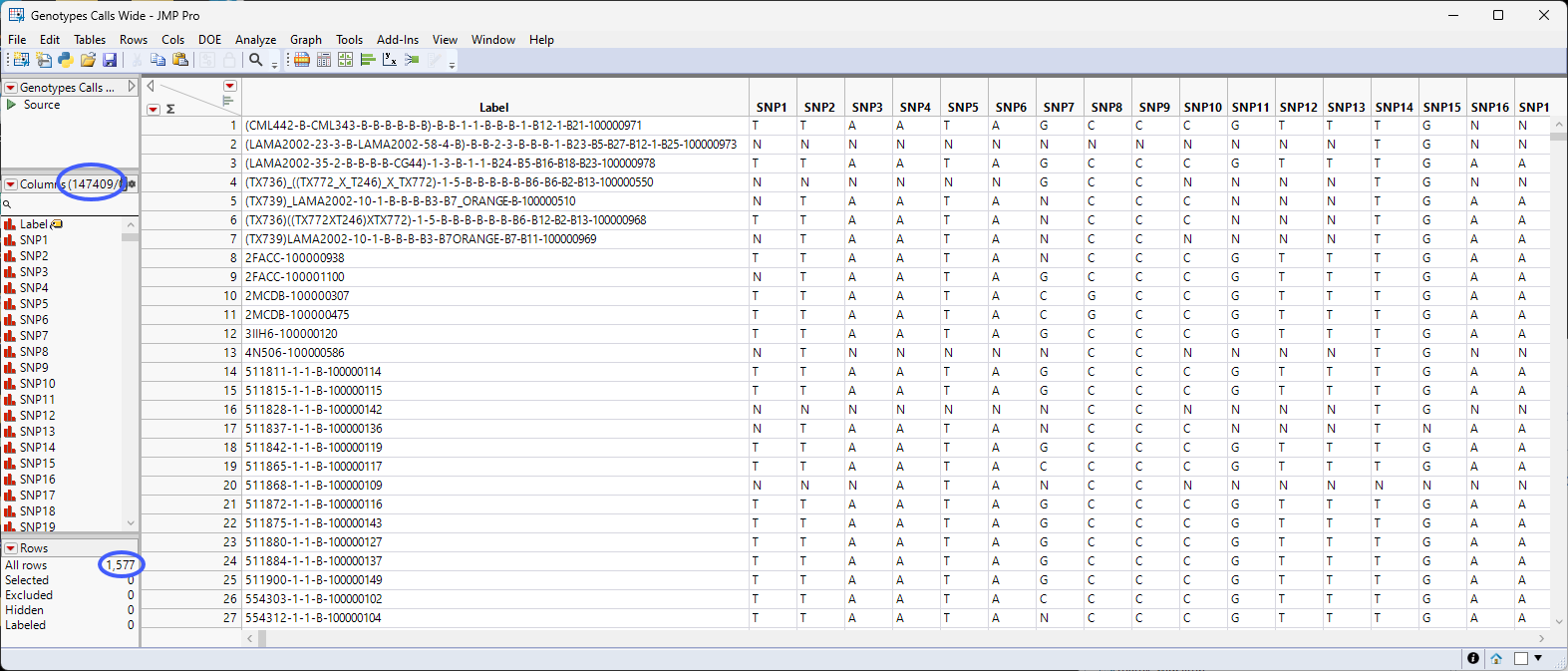
There are 147409 columns corresponding to the markers and 1577 rows corresponding to the number of sample files. The data is formatted in the single-nucleotide genotype format where genotype calls are listed in the one-letter IUPAC format.
Before we continue, let us discuss how genomic data should be structured for analysis in JMP Pro. Most of the processes in JMP Pro assume that the input table has a particular data structure.
First, JMP PRO distinguishes between tall and wide data sets. A tall data table has samples as columns and molecular entity (for example, markers, genes, clones, proteins, or metabolites) as rows, whereas a wide data table is the transpose of the tall, having the samples as rows and molecular entities as columns. When specifying the input data set for a process, it is important to know the required form. Most genomic analyses in JMP Pro require a wide data table.
The Genotypes_Calls_Wide.jmp data table is already in the wide format.
Another thing to consider is that Marker data must be encoded in the one-column, numerical, genotypic format. Typically, in this format, diploid individuals homozygous for the least common, or minor allele, are represented in the table by a “2”, whereas the heterozygotes are represented by a “1”. Homozygotes for the most common allele are represented by a “0”. This is not a common representation for genotypes. More typically, genotypes are represented by characters, either letters or numbers, often with both alleles represented with a delimiter. The genotype data in the Genotypes_Calls_Wide.jmp table are represented by single-nucleotide characters. This format is not recognized by JMP Pro and must be recoded to the numerical form before we can proceed with the analysis. Fortunately, in JMP Pro v19, an option has been added to the Marker Statistics platform that reads and converts character and other formats and converts them to the one-column, numerical, genotypic format.
• Select Analyze > Genetics > Marker Statistics.
• Select all the genotype columns as the Marker columns.
• Use the drop-down menu to select Single Code Nucleotide as the Marker Format.
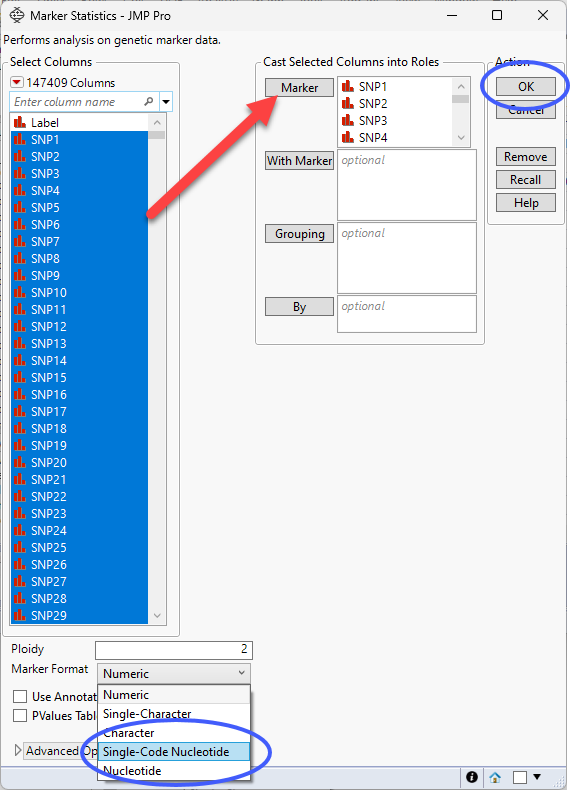
| 8 | Click . |
The Marker Statistics platform Duplicates the columns, placing the new columns at the end of the table, and recodes the format of the genotypes to numeric and runs the Marker Statistics analysis (not shown here). The new columns are identified by the num_ prefix.
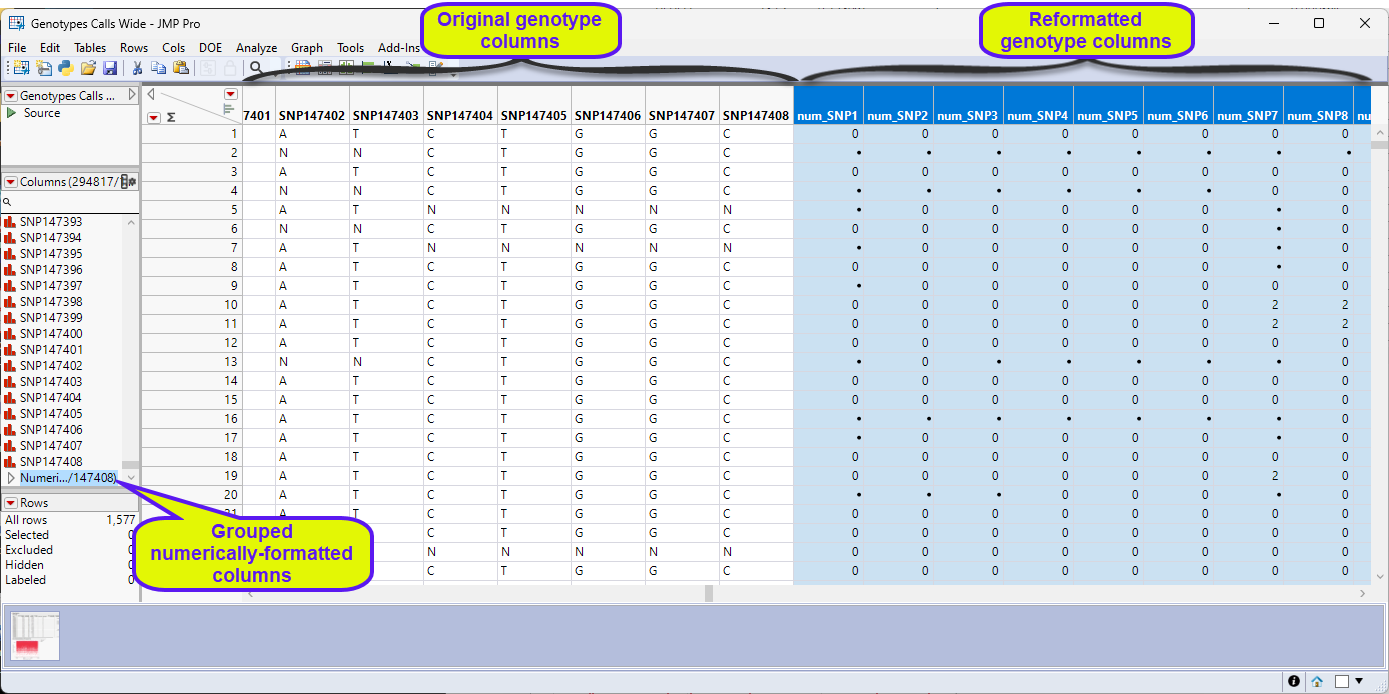
This file is ready for further analysis.
Note: You must use the recoded numeric columns for any analysis.
Importing Annotation Information
An Annotation data set can be generated from files within both the /Positions/ and /Genotypes/_Descriptors/ subdirectories using the same import process used to import the genotype data.
| 8 | Select File > Open. An Open Data File window opens to the last location used. |

It should open to the location of the ch01-g2f_2017_ZeaGBSv27_Imputed_AGPv4.h5 file and HDF5 Data Files should be selected as the file type.
• Click .
The Import HDF5 Tables window opens.

We are interested in the metadata files at the bottom of the file list. To generate and annotation file, we need to import selected metadata files; specifically, the MAF, SiteCoverage, AncestralAlleles, ChromosomeIndices, Chromosomes, Positions, ReferenceAlleles, and Snpids files.
• Hold down the CTRL key and select the files listed above.
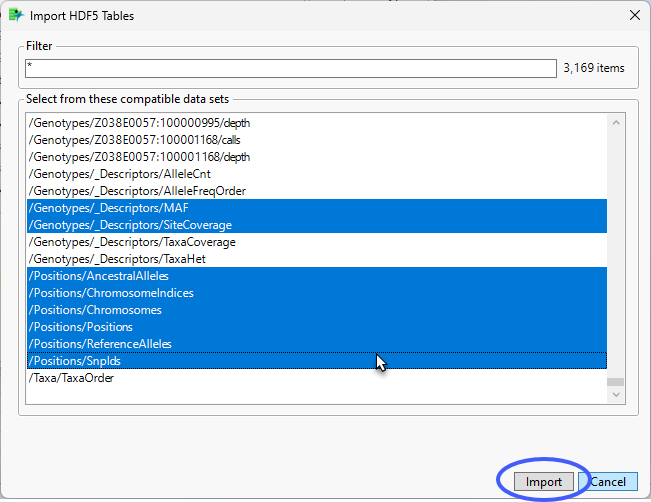
| 8 | Click . |
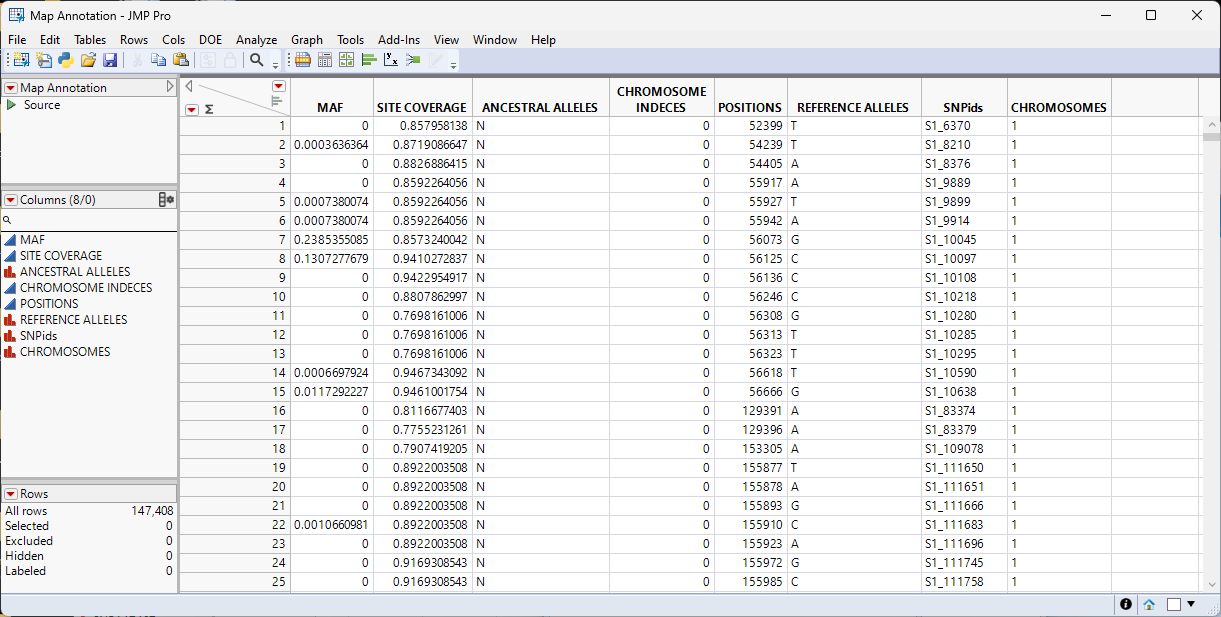
An annotation file is generated. There is a separate column for each file imported. This file is ready to use with the genotype data table for further analyses.