Hy’s Law Screening
This report visualizes peak values for lab measurements pertaining to Hy’s Law for detecting potential liver toxicity for all subjects across treatment arms. Lab measurements for Bilirubin (BILI), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) are divided by the upper limit of normal (ULN) and displayed in a scatterplot matrix annotated with Hy's Law reference lines (2*ULN of BILI, 3*ULN of ALT).
This analysis also creates reports of the distributions of relevant liver test variables, tables of missing tests and categorized liver elevation levels, and displays of the peak liver test values by Study day.
Note: This analysis can still be run on a blinded study but certain components of the reports are suppressed.
Note: JMP Clinical uses a special protocol for data including non-unique Findings test names. Refer to How does JMP Clinical handle non-unique Findings test names? for more information.
Report Results Description
Running this report with the Nicardipine sample setting generates the report shown below.
The Report contains the following elements:
Hy’s Law Screening
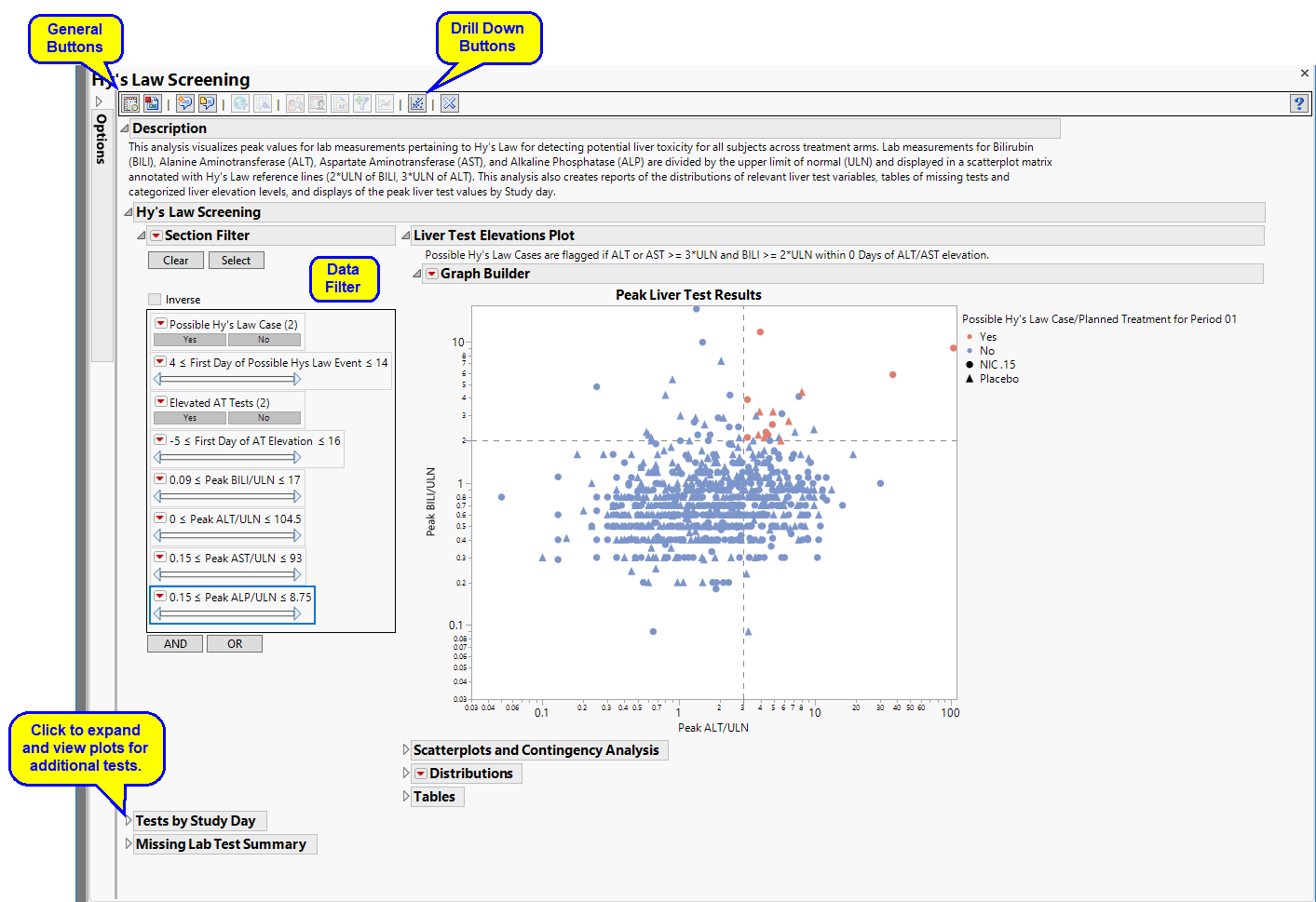
Displays an overall scatterplot of peak ALT, AST , BILI, and ALP measurements across the study, with color used to flag subjects meeting Hy's Law criteria.
The Hy’s Law Screening section consists of the following elements:
| • | One Overlay Plot of Hy's Law Lab Tests. |
This plot shows maximum laboratory values for the Alanine Aminotransferase ( ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase ( AST ), Total Bilirubin (BILI), and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) laboratory tests. The values are log2 transformed (this can be changed to log10 or no transformation in the report dialog) and normalized by the Upper Limit of Normal (LBSTNRHI). Reference lines are drawn by default at 3*ULN for ALT and AST and 2*ULN for BILI and ALP. These reference limits can be customized on the dialog.
These limits are also used to create the Hy's Law indicator flag. Subjects with a test value exceeding 3*ULN for ALT or AST (signs of hepatocellular injury) accompanied or followed by elevation of 2*ULN or greater for the BILI test have a "Yes" value for the Hy's Law Case variable created. A note defining the Hy's Law flag is located above the scatterplot matrix. For example, with the default settings the note is as follows: "Hys Law Cases are flagged if ALT or AST >= 3*ULN and BILI >= 2*ULN within 0 Days of ALT/AST peak." You can change the number of days following ALT/AST elevation for which to look for BILI elevation to flag possible Hy's Law cases on the report dialog. Subjects in the plot are colored by the Hy's Law criteria (red for "Yes", blue for "No") and marked by their treatment arm. You can choose to label the quadrants of Hy's Law (Cholestasis, Hy's Law, and Temple's Corollary) in the bottom left scatterplot through a check box option on the dialog.
Scatterplots
Displays scatterplots of peak ALT, AST, BILI, and ALP measurements across the study, with color used to flag subjects meeting Hy's Law criteria. Two contingency analyses show duration of Hy's Law and incidence of ALT or AST elevation by treatment.
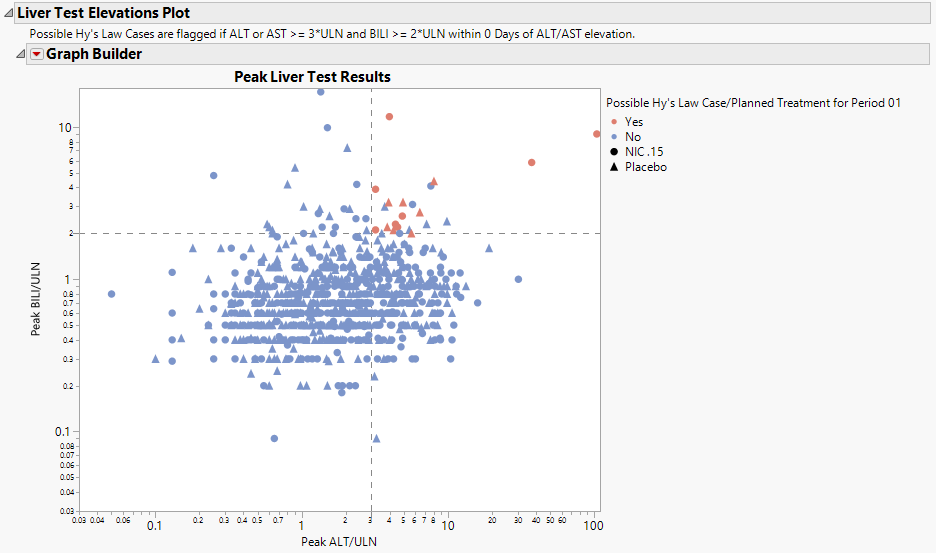
The Scatterplots section contains the following elements:
| • | One Scatterplot Matrix of Hy's Law Lab Tests. |
Tip: Adjust the size of the scatterplot matrix using the Frame Size slider, located at the upper left corner of the tab.
This plot shows maximum laboratory values for the Alanine Aminotransferase ( ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase ( AST ), Total Bilirubin (BILI), and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) laboratory tests. The values are log2 transformed (this can be changed to log10 or no transformation in the report dialog) and normalized by the Upper Limit of Normal (LBSTNRHI). Reference lines are drawn by default at 3*ULN for ALT and AST and 2*ULN for BILI and ALP. These reference limits can be customized on the dialog.
These limits are also used to create the Hy's Law indicator flag. Subjects with a test value exceeding 3*ULN for ALT or AST (signs of hepatocellular injury) accompanied or followed by elevation of 2*ULN or greater for the BILI test will have a "Yes" value for the Hy's Law Case variable created. A note defining the Hy's Law flag is located above the scatterplot matrix. For example, with the default settings the note is as follows: "Hys Law Cases are flagged if ALT or AST >= 3*ULN and BILI >= 2*ULN within 0 Days of ALT/AST peak." You can change the number of days following ALT/AST elevation for which to look for BILI elevation to flag possible Hy's Law cases on the report dialog. Subjects in the plot are colored by the Hy's Law criteria (red for "Yes", blue for "No") and marked by their treatment arm. You can choose to label the quadrants of Hy's Law (Cholestasis, Hy's Law, and Temple's Corollary) in the bottom left scatterplot through a check box option on the dialog.
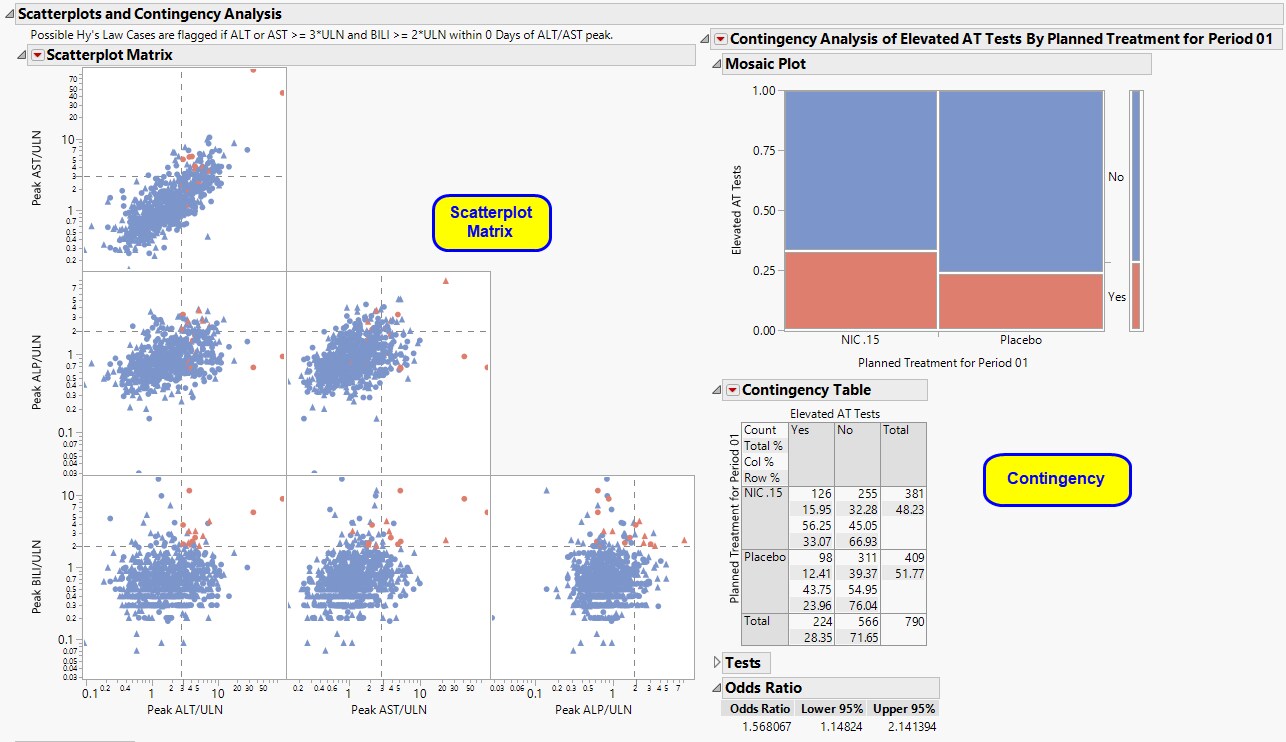
| • | One Contingency Analysis. |
One contingency analysis is shown in addition to the scatterplot matrix if any subjects were flagged as Hy's Law or if subjects experienced elevated ALT/AST tests. The first contingency analysis shows a Mosaic Plot and count matrix (Contingency Table) of how many days subjects were experiencing lab test elevations that met the Hy's Law flag across treatment arms. This plot and analysis can give valuable insight into the severity and duration of lab test elevation that could signify liver injury.
The Scatterplot Matrix and the Mosaic Plot in the Contingency Analyses are interactive and linked. You can select subjects in the scatterplot or in the colored boxes of the mosaic plot to see where they lie in the analysis. For example, it might be useful to select the boxes in the mosaic plot for the Days in Hy's Law contingency analysis for the treatment group to see the max lab values for those subjects in the scatterplots. In addition, you can select the points using the values of the Hy's Law Case and Treatment legend on the scatterplot. Once subjects are selected, you can choose from any of the Action Button -downs ( and are highly informative to look at the subjects' entire safety profiles) to further explore possibly liver injury safety issues in the trial.
Distributions
Displays a set of histograms and summary statistics for the Hy's Law case counts, first day of Hy's Law events, AT test counts and first day of elevation along with demographics.
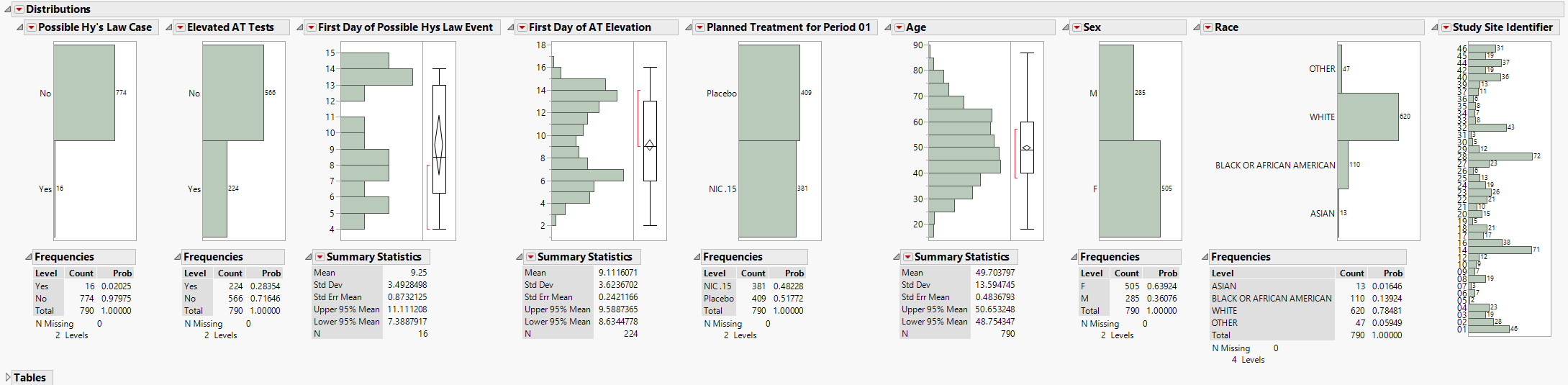
The Distributions section is shown above and contains the following elements:
| • | A set of Distributions. |
These display histograms and summary statistics of variables from the Findings data set that are relevant to a Hy’s Law analysis. Distributions of subjects on the Actual, Planned, or Specified Treatment (grouped by age, sex, race, and other factors) are displayed.
These distributions are useful for understanding the frequency and details of findings tests taken during a study. All distributions are linked: You can select bars in one histogram to see where those measurements fall in other findings variables shown on the display. Once you make selections, you can use the down buttons to down on those selected subjects.
Tables
Contains tables corresponding to AT Test Elevation and Potential Hy’s Law Cases, as well as counts and percentages for elevation categories for each liver test.
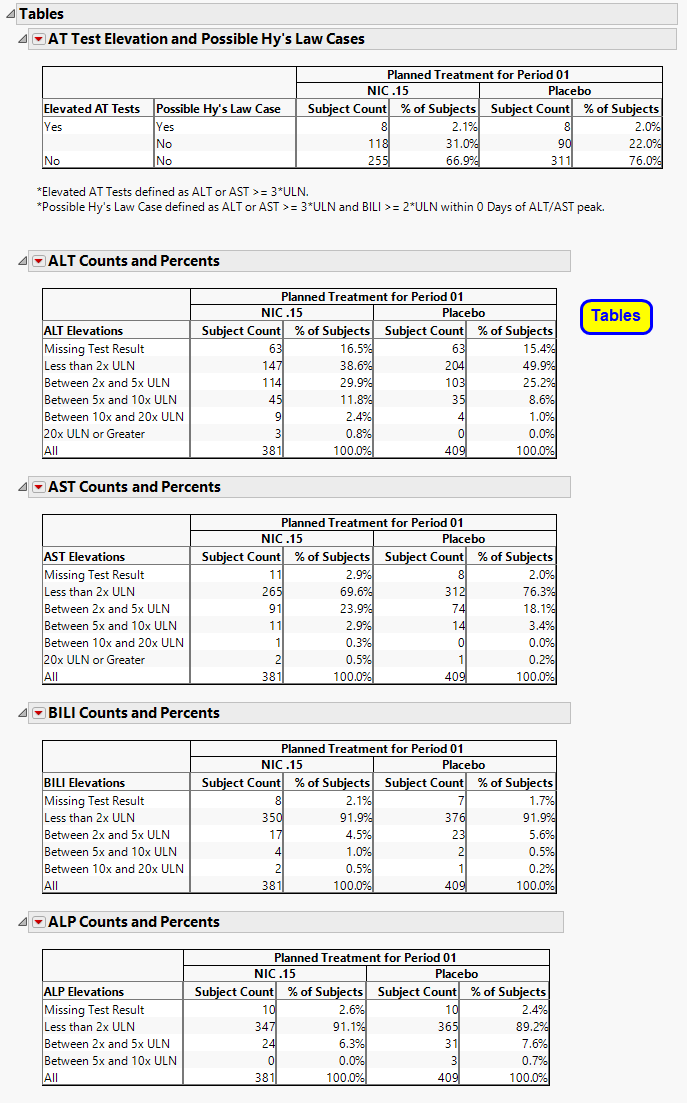
It contains the following elements:
| • | One AT Test Elevation and Potential Hy’s Law Cases table. |
Note: This table is shown only if at least one subject has a value of “Yes” for Elevated AT Tests.
This table lists subject count and percentages by treatment variable for subjects experiencing ALT or AST Elevation, or those defined as a Hy’s Law Case, or both.
| • | A table of Counts and Percents for elevation categories for each liver test. |
All tables are associated with the Local Data Filter (located on the right side). You can use this filter to subset the tables based on variable filters. You can select cells of these tables (either counts or percents) to select the corresponding rows in the data table.
Results for the various tests are sorted into rows as described in the following table::
|
Row |
Contains subjects who show results that are: |
|
Missing Test Result |
See below. |
|
Less than 2x ULN |
less than 2x the upper limit of normal (ULN) |
|
Between 2x and 5x ULN |
inclusive of greater than or equal to 2x ULN and less than 5x ULN |
|
Between 5x and 10x ULN |
inclusive of greater than or equal to 5x ULN and less than 10x ULN |
|
Between 10x and 20x ULN |
inclusive of greater than or equal to 10x ULN and less than 20x ULN |
Missing Test Result is calculated as count (and percent) of subjects who had no record of a specific test (there is no row in the lb data set for the respective LBTEST for the subject) at any day of the study, have no nonmissing measurement(s) for the recorded test (LBSTRESN is a missing value), or are missing the upper limit of normal reference limit (LBSTNRHI is a missing value).
Important: The counts and percentages for Missing Test Result on this section are calculated out of all subjects that have at least one nonmissing result for at least one of the liver lab tests. The counts shown on the Missing Lab Test Summary section include subjects that had no record or were missing all values for all four liver lab tests.
Note: These tables are derived from the same data table that the Hy’s Law Screening, Scatterplots, and Distributions sections are derived from, so any selections that you make are reflected across those tabs.
You can run downs off of table cell selections for an additional level of dynamic exploration.
Tests by Study Day
Displays a scatterplot matrix of four liver tests, plotting their peak values for each study day for each subject.
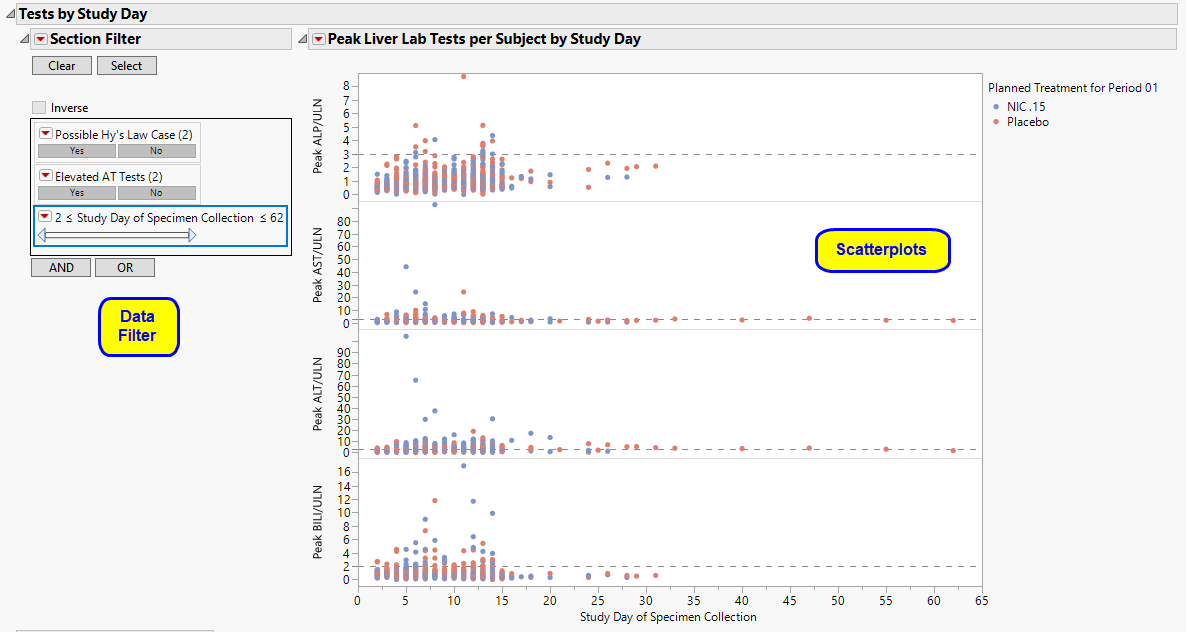
It contains the following elements:
| • | One Scatterplot Matrix of Peak Liver Lab Tests per Subject by Study Day. |
For each of the four liver tests, peak values are shown on the Y axis for each subject, for each Study Day (LBDY on the X axis). Points are colored by treatment group. Reference lines are drawn according to typical reference limits (or those custom reference lines specified on the report dialog).
In this example, you can inspect peak liver lab test values occurring on any study day of specimen collection, corresponding to the Nicardipine or Placebo planned treatment. Mouse over any point to view the corresponding unique subject identifier.
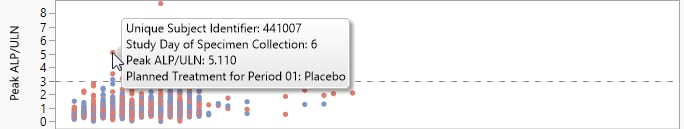
You can select points in the graph and their corresponding rows in the data table become selected. Click to see the data table reflecting any selections that you have made.
| • | One Data Filter. |
Use the data filter to subset the scatterplot matrix and associated data table by any of the available criteria. For example, you could filter the data by females between 40 and 50 years old. Drag the Age slider ends, or type over minimum and maximum age values to obtain an exact age range. The number of matching rows, selected graph points, and data table selections are updated accordingly.
Missing Lab Test Summary
Contains a table showing counts of subjects for which the relevant Hy's Law lab tests were not measured.

The Missing Lab Test Summary section contains the following elements:
| • | One table of Counts of Subjects Missing Liver Lab Records. |
This table lists counts of subjects across treatment arms for which the relevant liver tests were not performed or measured. It is common in clinical trials to measure these laboratory tests in order to monitor for potential liver injury.
| • | One table of Counts of Subjects Missing All Tests |
This table lists the number of subjects missing all 4 of the liver tests (ALP, ALT, AST, and BILI). This table is displayed only when there is at least 1 subject missing all four tests.
Important: The counts shown on this section include subjects that had no record or were missing all values for all four liver lab tests. The counts and percentages for Missing Test Result on the Tables section are calculated out of all subjects that have at least one nonmissing result for at least one of the liver lab tests.
The counts in the table columns are interactive. You can select the numbers to select the corresponding subjects for which a test was not measured. You can then use the Down Buttons to show those subjects or profile them for further analysis.
Section Filters
Each section includes a data filter that enables you to subset your data based on demographics, test results, and/or study site. Refer to Data Filter for more information about how to use the Data Filter.
Action Buttons
Action buttons, provide you with an easy way to drill down into your data. The following action buttons are generated by this report:
| • | Profile Subjects: Select subjects and click  to generate the patient profiles. See Profile Subjects for additional information. to generate the patient profiles. See Profile Subjects for additional information. |
| • | Show Subjects: Select subjects and click  to open the ADSL (or DM if ADSL is unavailable) of selected subjects. to open the ADSL (or DM if ADSL is unavailable) of selected subjects. |
| • | Cluster Subjects: Select subjects and click  to cluster them using data from available covariates. See Cluster Subjects for additional information. to cluster them using data from available covariates. See Cluster Subjects for additional information. |
| • | Demographic Counts: Select subjects and click  to create a data set of USUBJIDs, which subsets all subsequently run reports to those selected subjects. to create a data set of USUBJIDs, which subsets all subsequently run reports to those selected subjects. |
| • | Graph Time Profiles: Select subjects and click  to view a set of Hy’s Law Time Course Plots for each. to view a set of Hy’s Law Time Course Plots for each. |
| • | Liver Lab Shift Plots: Click  to launch and run liver labs (ALT, AST, ALP, BILI, or the LBTESTCD values that correspond to these tests) Shift Plots (and shift tables) via the Findings Shift Plots report on the data. This analysis currently runs using all subjects. to launch and run liver labs (ALT, AST, ALP, BILI, or the LBTESTCD values that correspond to these tests) Shift Plots (and shift tables) via the Findings Shift Plots report on the data. This analysis currently runs using all subjects. |
General
| • | Click  to view the associated data tables. Refer to View Data for more information. to view the associated data tables. Refer to View Data for more information. |
| • | Click  to generate a standardized pdf- or rtf-formatted report containing the plots and charts of selected sections. to generate a standardized pdf- or rtf-formatted report containing the plots and charts of selected sections. |
| • | Click  to take notes, and store them in a central location. Refer to Add Notes for more information. to take notes, and store them in a central location. Refer to Add Notes for more information. |
| • | Click  to read user-generated notes. Refer to View Notes for more information. to read user-generated notes. Refer to View Notes for more information. |
| • | Click  to open and view the Subject Explorer/Review Subject Filter. to open and view the Subject Explorer/Review Subject Filter. |
| • | Click  to specify Derived Population Flags that enable you to divided the subject population into two distinct groups based on whether they meet very specific criteria. to specify Derived Population Flags that enable you to divided the subject population into two distinct groups based on whether they meet very specific criteria. |
| • | Click the arrow to reopen the completed report dialog used to generate this output. |
| • | Click the gray border to the left of the Options tab to open a dynamic report navigator that lists all of the reports in the review. Refer to Report Navigator for more information. |
Report Options
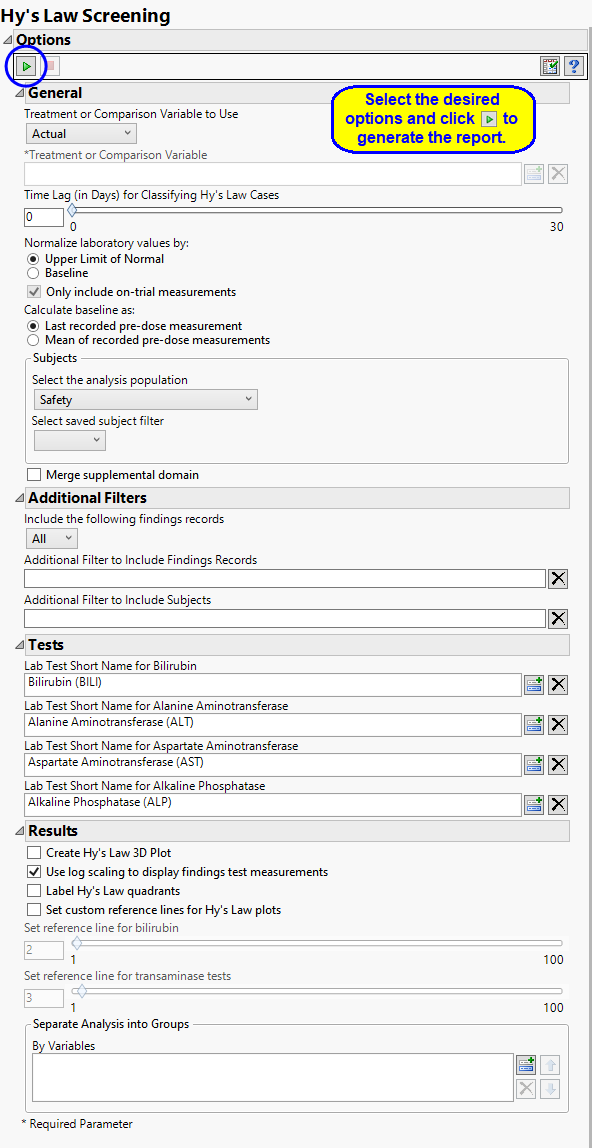
This report requires lab results for bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and alkaline phosphatase. At least one of the standardized short name character strings listed in the following table must be present in the LBTESTCD column for each lab result.
|
Lab Test1: |
Required String: |
|
Bilirubin |
Either BILI or TBIL Note: If neither BILI nor TBIL are found, the report searches for and uses TBILI, TBL, BILT, BILTOT, and BIL (in that order). |
|
Alanine Aminotransferase |
Either ALT, ALAT, or SGPT |
|
Aspartate Aminotransferase |
Either AST, ASAT, or SGOT |
|
Alkaline Phosphatase |
Either ALP or ALKP Note: If neither ALP nor ALKP are found, the report searches for and uses ALK and APH, in that order. |
Treatment or Comparison Variable:
The primary goal of clinical trials is to distinguish treatment effects when reporting and analyzing trial results. Treatments are defined by specific values in the treatment or comparison variables of the CDISC models. These variables are specified in this report using the Treatment or Comparison Variable to Use andTreatment or Comparison Variable options.
Distributions of the specified treatment or comparison variables are shown in the output.
Available variables include Planned, which is selected when the treatments patients received exactly match what was planned and Actual, which is selected when treatment deviates from what was planned.
You can also specify a variable other than the ARM or TRTxxP (planned treatment) or ACTARM or TRTxxA (actual treatment) from the CDISC models as a surrogate variable to serve as a comparator. Finally you can select None to plot the data without segregating it by a treatment variable.
See Treatment or Comparison Variable to Use, Treatment or Comparison Variable for more information.
General Options
Use the Time Lag (in Days) for Classifying Hy’s Law Cases option to specify the allowed interval between transaminase and bilirububin measurements for a patient to be considered a Hy’s Law case. The default value of 0 days indicates that a subject is a Hy’s Law case if Transaminase measurements (ALT or AST) exceed 3 times the upper limit of normal (3*ULN) and Total Bilirubin measurements exceed twice the specified ULN (2*ULN) from tests taken on the same study day. Alternatively, a time lag can be set to x number of days to classify a subject as a Hy's Law Case if Total Bilirubin exceeds 2*ULN within x days after ALT or AST exceeds 3*ULN.
For example, this value can be set to 30 in order to flag subjects as Hy's Law cases if a subject has BILI >= 2*ULN at any time within a month after elevated Transaminase measurements above 3*ULN.
You can choose to normalize the measurements by either the ULN or the baseline measurements for each test. You can select either the last pre-dose values or the means of all pre-dose values as the baseline See Use the Normalize laboratory values by: and Calculate baseline as: for more information.
The Only include on-trial measurements option filters out any screening/baseline measurements (anything flagged with a baseline flag or that occurs on or before Study Day 1) so that only on-trial measurements are considered for the Hy's law calculation. This option is checked by default and is applied when values are normalized by ULN. If you uncheck this option or choose to normalize laboratory values by the baseline all measurements are included.
Filtering the Data:
Filters enable you to restrict the analysis to a specific subset of subjects and/or findings records, based on values within variables. You can also filter based on population flags (Safety is selected by default) within the study data.
If there is a supplemental domain (SUPPXX) associated with your study, you can opt to merge the non-standard data contained therein into your data.
See Select the analysis population, Select saved subject filter2, Merge supplemental domain, Include the following findings records:, Additional Filter to Include Findings Records, and Additional Filter to Include Subjects3 or more information.
Tests
Use this text fields to specify the Test Short Name (LBTESTCD ) value that corresponds to each of the tests associated with Hy’s Law screening. These include tests for bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and alkaline phosphatase. These options are enable you to specify individual tests when non-standard test names are used in the study. If these options are left blank, JMP Clinical uses the standard test designations.
See Lab Test Short Name for Bilirubin, Lab Test Short Name for Alanine Aminotransferase, Lab Test Short Name for Aspartate Aminotransferase, and Lab Test Short Name for Alkaline Phosphatase for more information.
Results
These options enable you to adjust the report according to the needs of your organization.
Selecting Create Hy’s Law 3D Plot generates an interactive 3 dimensional plot showing the ratios of bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase, and apartate aminotransferase to their respective upper limits of normal (ULN) values.
Selecting Use log scaling to display findings test measurements converts the axes of all plots to log-scale. Note: This option is selected by default.
Selecting Label Hy’s Law quadrants places identifying labels, relating to Hy’s law, in each quadrant of all of the plots of bilirubin versus alanine aminotransferase.
Use the Set custom reference lines for Hy’s Law plots option to draw reference lines on the Hy’ Law plots. You must then use the Set reference line for bilirubin option to specify the value by which to multiply the ULN for bilirubin and/or alkaline phosphatase. By default, this value is set to 2 or twice the ULN. You must also use the Set reference line for transaminase tests option to specify the value by which to multiply the ULN for alanine and/or aspartate transaminase. By default. this value is set to 3 or 3x the ULN.
You can also subdivide the subjects and run analyses for distinct groups by specifying one or more By Variables.