Review Status Distribution
This report shows the distribution of the review status of subjects in a study.
Before you can run this report, you must have identified and analyzed data from patients of interest, and indicated review status using the Profile Subjects report.
Report Results Description
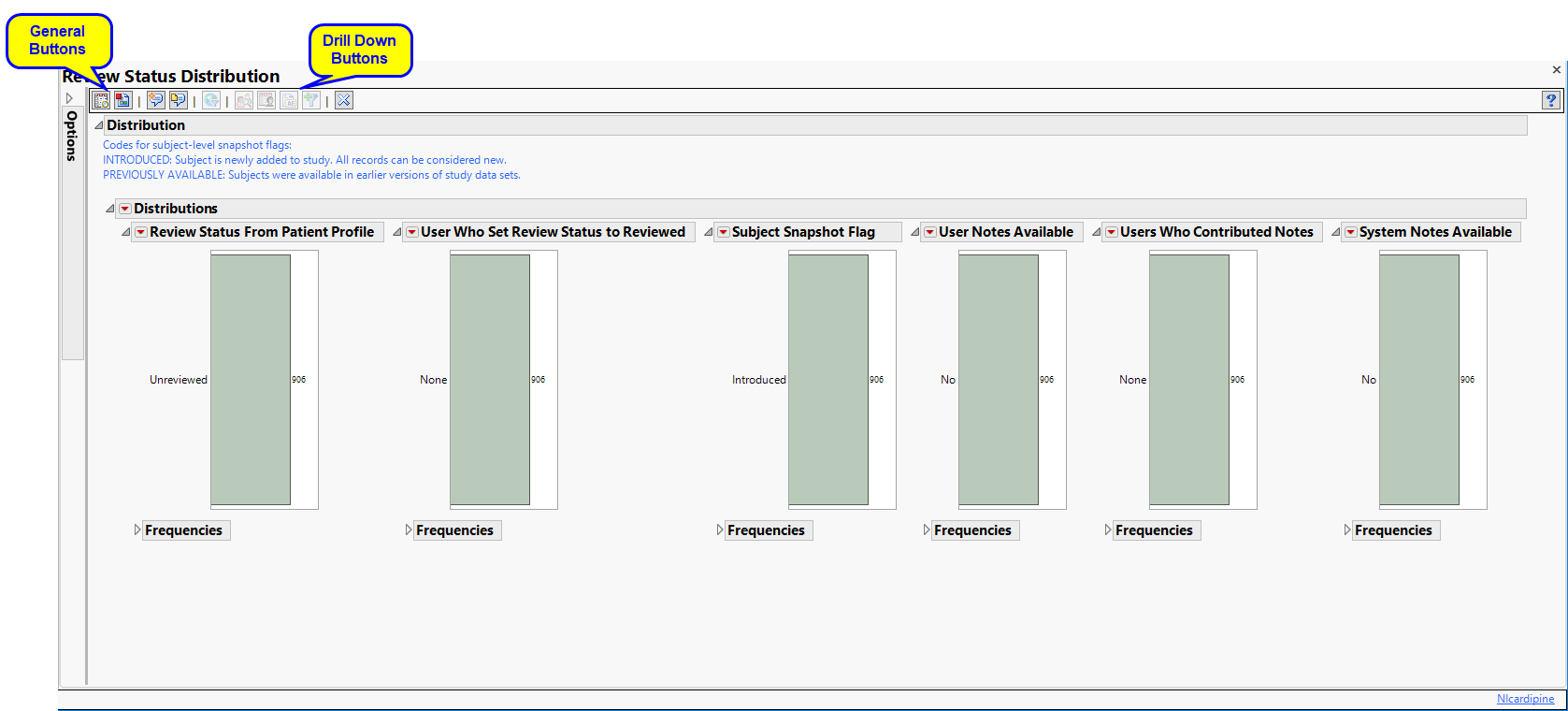
Running this report for the Nicardipine sample setting generates the report shown below.
 [
[
The report contains the following elements:
Distributions
Displays summary statistics for review status (reviewed or unreviewed), review flag, and user and system note availability. These statistics can be changed when reviewing subjects from the Patient Profiler.
The Distribution section contains the following elements:
| • | Six Histograms, detailing counts and proportions for review status (reviewed or unreviewed) and who set that status, review flag (introduced, new record, modified record, or stable), and availability of user and system notes, including who contributed the notes. |
Review status can be changed when reviewing subjects from the Patient Profiler. In this example, 4 out of 902 subjects (0.4%) have been reviewed in the Patient Profiler, all have been newly added to the review, none of them have user notes, and 100 subjects (11.1%) have system notes.
Note: The review flag of a reviewed subject who is found to have new or modified records with a snapshot update is switched to unreviewed.
Note: System notes are automatically generated to record the time stamp of study creation and modification events.
Action Buttons
Action buttons, provide you with an easy way to drill down into your data. The following action buttons are generated by this report:
| • | Profile Subjects: Select subjects and click  to generate the patient profiles. See Profile Subjects for additional information. to generate the patient profiles. See Profile Subjects for additional information. |
| • | Show Subjects: Select subjects and click  to open the ADSL (or DM if ADSL is unavailable) of selected subjects. to open the ADSL (or DM if ADSL is unavailable) of selected subjects. |
| • | Cluster Subjects: Select subjects and click  to cluster them using data from available covariates. See Cluster Subjects for additional information. to cluster them using data from available covariates. See Cluster Subjects for additional information. |
| • | Demographic Counts: Select subjects and click  to create a data set of USUBJIDs, which subsets all subsequently run reports to those selected subjects. The currently available filter data set can be applied by selecting Apply Subject Filter in any report dialog. to create a data set of USUBJIDs, which subsets all subsequently run reports to those selected subjects. The currently available filter data set can be applied by selecting Apply Subject Filter in any report dialog. |
General
| • | Click  to view the associated data tables. Refer to View Data for more information. to view the associated data tables. Refer to View Data for more information. |
| • | Click  to generate a standardized pdf- or rtf-formatted report containing the plots and charts of selected sections. to generate a standardized pdf- or rtf-formatted report containing the plots and charts of selected sections. |
| • | Click  to take notes, and store them in a central location. Refer to Add Notes for more information. to take notes, and store them in a central location. Refer to Add Notes for more information. |
| • | Click  to read user-generated notes. Refer to View Notes for more information. to read user-generated notes. Refer to View Notes for more information. |
| • | Click  to open and view the Subject Explorer/Review Subject Filter. to open and view the Subject Explorer/Review Subject Filter. |
| • | Click  to specify Derived Population Flags that enable you to divided the subject population into two distinct groups based on whether they meet very specific criteria. to specify Derived Population Flags that enable you to divided the subject population into two distinct groups based on whether they meet very specific criteria. |
| • | Click the arrow to reopen the completed report dialog used to generate this output. |
| • | Click the gray border to the left of the Options tab to open a dynamic report navigator that lists all of the reports in the review. Refer to Report Navigator for more information. |
Report Options
Treatment or Comparison Variable:
The primary goal of clinical trials is to distinguish treatment effects when reporting and analyzing trial results. Treatments are defined by specific values in the treatment or comparison variables of the CDISC models. These variables are specified in this report using the Treatment or Comparison Variable to Use andTreatment or Comparison Variable options.
Distributions of the specified treatment or comparison variables are shown in the output.
Available variables include Planned, which is selected when the treatments patients received exactly match what was planned and Actual, which is selected when treatment deviates from what was planned.
You can also specify a variable other than the ARM or TRTxxP (planned treatment) or ACTARM or TRTxxA (actual treatment) from the CDISC models as a surrogate variable to serve as a comparator. Finally you can select None to plot the data without segregating it by a treatment variable.
See Treatment or Comparison Variable to Use, Treatment or Comparison Variable for more information.
Filtering the Data:
Filters enable you to restrict the analysis to a specific subset of subjects.
Note: Subjects not meeting filtering criteria remain in the domains but notes associated with them are not surfaced in the viewer.
See Select saved subject filter1, and Additional Filter to Include Subjects for more information.