Create Light Sources
Light sources are specifications of a color, position, and direction. JSL allows for up to eight lights (numbered 0 to 7) defined by the Light function, where n is the number of the light.
Light( n, argument, value, ... value )
Note: To turn each light on, issue an Enable(Lighting) and an Enable(lightn) function, where n is the light number. Then, move the light to a position in the scene with a Light(n, POSITION, x, y, z) function.
The value of argument can be any one of those shown in Table 13.3. The table shows default values for each argument.
|
Argument |
Default Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
AMBIENT |
(0, 0, 0, 1) |
Ambient RGBA intensity |
|
DIFFUSE |
(1, 1, 1, 1) |
diffuse RGBA intensity |
|
SPECULAR |
(1, 1, 1, 1) |
specular RGBA intensity |
|
POSITION |
(0, 0, 1, 0) |
(x, y, z, w) position |
|
SPOT_DIRECTION |
(0, 0, -1) |
(x, y, z) direction of spotlight |
|
SPOT_EXPONENT |
0 |
spotlight exponent |
|
SPOT_CUTOFF |
180 |
spotlight cutoff angle |
|
CONSTANT_ATTENUATION |
1 |
constant attenuation factor |
|
LINEAR_ATTENUATION |
0 |
linear attenuation factor |
|
QUADRATIC_ATTENUATION |
0 |
quadratic attenuation factor |
Note: The default values for DIFFUSE and SPECULAR in this table apply only to Light 0. For other lights, the default value is (0, 0, 0, 1) for both arguments.
The first three arguments (AMBIENT, DIFFUSE, and SPECULAR) are used to color the light. DIFFUSE is the argument that is most closely associated with the physical color of the light. AMBIENT refers to the property of the light when it functions as a background light. SPECULAR alters the way a light is reflected off a surface.
Specify the position of the light using the POSITION argument. Nonzero values of the fourth (w) coordinate position the light in homogenous object coordinates.
Light in the real-world decreases in intensity as distance from the light increases. Since a directional light is infinitely far away, it does not make sense to attenuate its intensity as a function of distance. However, JSL attenuates a light source by multiplying the contribution of the source by an attenuation factor
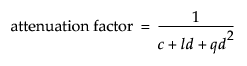
where c = CONSTANT_ATTENUATION, l = LINEAR_ATTENUATION, and q = QUADRATIC_ATTENUATION.
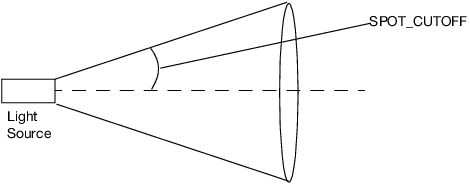
To create a spotlight, limit the shape of the light to a cone. Use the SPOT_CUTOFF argument to define the side of the cone, as shown in the following illustration.
Figure 13.16 Spotlight
In addition to the cutoff angle, you can control the intensity and direction of the light distribution in the cone. SPOT_DIRECTION specifies the direction for the spotlight to point; SPOT_EXPONENT influences how concentrated the light is.