Launch the Text Explorer Platform
Launch the Text Explorer platform by selecting Analyze > Text Explorer.
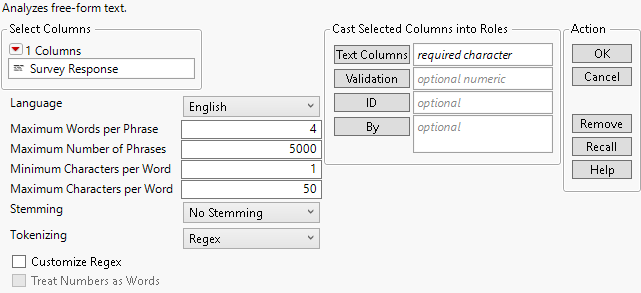
Figure 12.6 The Text Explorer Launch Window
For more information about the options in the Select Columns red triangle menu, see Column Filter Menu in Using JMP. The Text Explorer launch window contains the following options:
Text Columns
Assigns the columns that contain text data. If you specify multiple columns, a separate analysis is created for each column.
 Validation
Validation
In JMP Pro, you can enter a Validation column. If you click the Validation button with no columns selected in the Select Columns list, you can add a validation column to your data table. For more information about the Make Validation Column utility, see Make Validation Column in Predictive and Specialized Modeling.
The specification of a Validation column does not affect the calculation of the document-term matrix. However, when a Validation column is specified, only the training set is used for the Latent Class Analysis, Latent Semantic Analysis, Topic Analysis, and Discriminant Analysis options. The Validation column is used as the Generalized Regression validation method for the Term Selection option.
ID
Assigns a column used to identify separate respondents in the Save Stacked DTM for Association output data table. This output data table is suitable for association analysis. This column is also used to identify separate respondents in the Latent Class Analysis report.
By
Identifies a column that creates a report consisting of separate analyses for each level of the variable. If more than one By variable is assigned, a separate report is produced for each possible combination of the levels of the By variables.
Note: If you specify a By variable, the Customize Regex option and settings apply to all levels of the By variables.
Language
Specifies the language used for text processing. This affects stemming and the built-in lists of stop words, recodes, and phrases. This option is independent of the language in which JMP is running. Unless the Language platform preference is set, the Language option is set according to the JMP Display Language preference.
Note: When Japanese, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), or Korean is specified as the Language option, JMP uses a language-specific dictionary of words to parse the text. The dictionary is downloaded from a public source and stored in a JMP data table the first time that you specify any of the above languages. You can also add or remove words from the language-specific dictionary. See Tokenizing Stage for Asian Languages.
Maximum Words per Phrase
Specifies a maximum number of words that a phrase can contain to be included as a phrase in the analysis.
Maximum Number of Phrases
Specifies the maximum number of phrases that appear in the phrase list.
Minimum Characters per Word
Specifies the number of characters that a word must contain to be included as a term in the analysis.
Maximum Characters per Word
Specifies the largest number of characters (up to 2000) that a word can contain to be included as a term in the analysis.
Stemming
(Available only when the Language option is set to English, German, Spanish, French, or Italian.) Specifies a method for combining terms with similar beginning characters but different endings. The following options are available:
No Stemming
No terms are combined.
Stem for Combining
Stems only the terms where two or more terms stem to the same term.
Stem All Terms
Stems all terms.
Note: The use of the Stemming option also affects phrases that have been added to the term list. Phrase identification occurs after terms within a phrase have been stemmed. For example, “dogs bark” and “dog barks” would both match the specified phrase “dog· bark·”. Phrases cannot be removed from the term list when a Stemming option is selected.
Tokenizing
(Available only when the Language option is set to English, German, Spanish, French, or Italian.) Specifies a method for parsing the text into terms or tokens. The following tokenization options are available:
Regex
Parses text using a default set of built-in regular expressions. If you want to add to, remove, or edit the set of regular expressions used to parse the text, select the Customize Regex option. See Customize Regex in the Regular Expression Editor.
Basic Words
Text is parsed into words based on a set of characters that typically separate words. These characters include spaces, tabs, new lines, and most punctuation marks. If you want numbers to be parsed into terms for the analysis, select the Treat Numbers as Words option. If you do not select this option, pieces of text between delimiters that contain only numbers are ignored in the tokenizing step.
Tip: You can view the default set of delimiters using the Display Options > Show Delimiters option in a Text Explorer report that uses the Basic Words Tokenizing method.
Customize Regex
(Available only with the Regex Tokenizing method.) Enables you to use the Text Explorer Regular Expression Editor window to modify the Regex settings. Use this option to accommodate non-traditional words. Examples include phone numbers or words formed by a combination of characters and numbers. Using the Customize Regex option is not recommended unless the default Regex method is not giving you the results that you need. This can happen when your text contains structures that the default Regex method does not recognize. See Customize Regex in the Regular Expression Editor.
Treat Numbers as Words
(Available only with the Basic Words Tokenizing method.) Allows numbers to be tokenized as terms in the analysis. When this option is selected, the Minimum Characters per Word setting is ignored for terms that contain numeric digits.
After you click OK on the launch window, the Text Explorer Regular Expression Editor window appears if you selected Customize Regex in the launch window. Otherwise, the Text Explorer report appears.
Note: The processing of text input is not case-sensitive. All text is converted to lowercase internally prior to tokenization and all analysis steps. This conversion affects the processing of regular expressions and the aggregation of terms in the Text Explorer output.