 Mixed Model Report and Options
Mixed Model Report and Options
The Mixed Model red triangle menu contains the following options:
Model Reports
Produces reports that relate to the mixed model fit. These reports give estimates and tests for model parameters, as well as fit statistics.
Fit Statistics
Shows or hides a report for model fit statistics. See Fit Statistics.
Random Effects Covariance Parameter Estimates
(Available only when there are random effects specified in the launch window.) Shows or hides a report of random effects covariance parameter estimates. See Random Effects Covariance Parameter Estimates.
Fixed Effects Parameter Estimates
Shows or hides a report of fixed effects parameter estimates. See Fixed Effects Parameter Estimates.
Repeated Effects Covariance Parameter Estimates
(Available only when there are repeated effects specified in the launch window.) Shows or hides a report of repeated effects covariance parameter estimates. See Repeated Effects Covariance Parameter Estimates.
Random Coefficients
(Available only when there are random effects specified in the launch window.) Shows or hides a report of random coefficients. See Random Coefficients.
Random Effects Predictions
(Available only when there are random effects specified in the launch window.) Shows or hides a report of random effect predictions. See Random Effects Predictions.
Indicator Parameterization Estimates
(Available only when there are nominal columns among the fixed effects and the model contains an intercept.) Shows or hides the Indicator Function Parameterization report. This report gives parameter estimates for the fixed effects based on a model where nominal fixed effect columns are coded using indicator (SAS GLM) parameterization and are treated as continuous. Ordinal columns remain coded using the usual JMP coding scheme. The SAS GLM and JMP coding schemes are described in The Factor Models.
Caution: Standard errors, t-ratios, and other results given in the Indicator Function Parameterization report differ from those in the Parameter Estimates report. This is because the estimates are estimating different parameters.
Fixed Effects Test
(Available only for models that contain at least one fixed effect.) Shows or hides the tests of fixed effects. See Fixed Effects Tests.
Sequential Tests
(Available only for models that contain at least one fixed effect.) Shows or hides the Sequential (Type 1) Tests report that contains the sums of squares as effects are added to the model sequentially. Conducts F tests based on the sequential sums of squares. See Sequential Tests.
Multiple Comparisons
Opens the Multiple Comparisons launch window where you can select one or more effects and initial comparisons. This report is available for categorical fixed effects. See Multiple Comparisons.
Linear Combination of Variance Components
(Not available when there are no G-side effects.) Shows a report that enables you to compute confidence intervals for linear combinations of variance components. Initially, the report contains an editable text box and a table of variance components in the model. Use the text box to label the linear combination. Enter values in the cells in the right column of the table to specify the linear functions for your confidence intervals. After you specify a linear combination of parameters and click Done, a table appears that contains confidence intervals for the specified linear combination.
The table contains an estimate and standard error, as well as two types of confidence intervals (Satterthwaite and Wald) and a Wald p-value. The Wald p-value corresponds to a hypothesis test that the estimate differs from zero.
Tip: The Satterthwaite confidence interval is restricted to positive values, so it is not recommended for cases where the specified coefficients are negative. If the estimate is negative, the Satterthwaite confidence interval cannot be constructed and is reported as missing.
Compare Slopes
(Available only when there is one nominal term, one continuous term, and their interaction effect for the fixed effects.) Shows or hides a report that enables you to compare the slopes of each level of the interaction effect in an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model. See Compare Slopes.
Inverse Prediction
(Available only when there is at least one continuous fixed effect term and there is a residual variance term.) For one or more values of the response, predicts values of explanatory variables. See “Inverse Prediction”.
Marginal Model Inference
Shows or hides plots that are based on marginal predicted values and marginal residuals. These plots display the variation due to random effects.
Actual by Predicted Plot
Plots actual values versus values predicted by the model, but without accounting for the random effects. The Actual by Predicted Plot appears by default. See Actual by Predicted Plot.
Residual Plots
Provides residual plots that assess model fit, without accounting for the random effects. See Residual Plots.
Profiler, Contour Profiler, Mixture Profiler, Surface Profiler
Provides profilers to examine the relationship between the response and the model terms, without accounting for random effects. See Marginal Model Profiler.
Variogram
Provides a variogram plot that shows the change in covariance as the distance between observations increases. When the Residual structure is selected, you can select the columns to use as temporal or spatial coordinates. See Variogram.
Conditional Model Inference
Shows or hides plots that are based on conditional predicted values and conditional residuals. These plots display the variation that remains, once random effects are accounted for.
Actual by Conditional Predicted Plot
Plots actual values versus values predicted by the model, accounting for the random effects. When there are random effects, the Actual by Conditional Predicted Plot appears by default. See Actual by Conditional Predicted Plot.
Conditional Residual Plots
Provides residual plots that assess model fit, accounting for the random effects. See Conditional Residual Plots.
Conditional Profiler, Conditional Contour Profiler, Conditional Mixture Profiler, Conditional Surface Profiler
Provides profilers to examine the relationship between the response and the model terms, accounting for random effects. See Conditional Profilers.
Covariance and Correlation Matrices
Contains options to view the covariance and correlation matrices that are associated with the model.
Covariance of Fixed Effects
Shows or hides the covariance matrix for the fixed effects in the model.
Covariance of Covariance Parameters
Shows or hides the covariance matrix for the random effects in the model. The effects in the matrix are ordered as follows: G-side random effects, R-side random effects, and residual effects.
Covariance of All Parameters
Shows or hides the covariance matrix for all effects in the model. The effects in the matrix are ordered as follows: fixed effects, G-side random effects, R-side random effects, and residual effects.
Correlation of Fixed Effects
Shows or hides the correlation matrix for the fixed effects in the model.
Repeated Measures Covariance Diagnostics
(Available only for models that specify an unstructured repeated covariance structure.) Shows or hides a report that contains diagnostic tools to help determine candidate covariance structures for the repeated measures analysis. The report contains the covariance matrix and correlation matrix of the repeated measures parameters. The report also contains a heat map of the correlations. The scale of the heat map is determined by the range of the correlations. If all the correlations are positive, the scale is 0 to 1; otherwise, the scale is -1 to 1.
Save Columns
Contains options to save various model results as columns in the data table.
Prediction Formula
Creates a new column called Pred Formula <colname> that contains both the formula and the marginal mean predicted values. A Predicting column property is added, noting the source of the prediction. See Marginal Model Inference.
Standard Error of Predicted
Creates a new column called StdErr Pred <colname> that contains standard errors for the predicted marginal mean responses.
Mean Confidence Interval
Creates two new columns called Lower 95% Mean <colname> and Upper 95% Mean <colname>. These columns contain the lower and upper 95% confidence limits for the mean response. These intervals include the variation in the estimation, but not in the response. You can change the α level in the Fit Model window by selecting Set Alpha Level from the Model Specification red triangle menu.
Indiv Confidence Interval
(Available for models that contain only G-side effects.) Creates two new columns called Lower 95% Indiv <colname> and Upper 95% Indiv <colname>. These columns contain lower and upper 95% confidence limits for individual response values. These intervals include the variation in both the response and its estimation. You can change the α level in the Fit Model window by selecting Set Alpha Level from the Model Specification red triangle menu.
Residuals
Creates a new column called Residual <colname> that contains the observed response values minus their marginal mean predicted values. See Marginal Model Inference.
Conditional Prediction Formula
Creates a new column called Cond Pred Formula <colname> that contains both the formula and the conditional mean predicted values. A Predicting column property is added, noting the source of the prediction. See Conditional Profilers.
Standard Error of Conditional Predicted
Creates a new column called StdErr Cond Pred <colname> that contains standard errors for the predicted conditional mean responses.
Conditional Mean CI
(Available for models that contain a G-side effect.) Creates two new columns called Lower 95% Cond Mean <colname> and Upper 95% Cond Mean <colname>. These columns contain the lower and upper 95% confidence limits for the expected value from conditional prediction. The confidence intervals include random effect estimates for models with random effects. See Conditional Model Inference. You can change the α level in the Fit Model window by selecting Set Alpha Level from the Model Specification red triangle menu.
Conditional Residuals
Creates a new column called Cond Residual <colname> that contains the observed response values minus their conditional mean predicted values. See Conditional Model Inference.
Save Simulation Formula
(Available only for variance component and random coefficient models. Not available when a By variable is specified in the Fit Model launch window.) Saves a column to the data table that contains a formula that generates simulated values using the estimated parameters for the model that you fit. This column can be used in the Simulate utility as a Column to Switch In. See Simulate in Basic Analysis.
Model Dialog
Opens the completed Fit Model launch window for the current analysis. See Fit Model Launch Window.
See Local Data Filters in JMP Reports, Redo Menus in JMP Reports, Save Platform Preferences, and Save Script Menus in JMP Reports in Using JMP for more information about the following options:
Local Data Filter
Shows or hides the local data filter that enables you to filter the data used in a specific report.
Redo
Contains options that enable you to repeat or relaunch the analysis. In platforms that support the feature, the Automatic Recalc option immediately reflects the changes that you make to the data table in the corresponding report window.
Platform Preferences
Contains options that enable you to view the current platform preferences or update the platform preferences to match the settings in the current JMP report.
Save Script
Contains options that enable you to save a script that reproduces the report to several destinations.
Save By-Group Script
Contains options that enable you to save a script that reproduces the platform report for all levels of a By variable to several destinations. Available only when a By variable is specified in the launch window.
 Fit Statistics
Fit Statistics
The Fit Statistics report in the Mixed Model personality provides statistics used for model comparison. For all fit statistics, smaller is better. A likelihood ratio test between two models can be performed if one model is contained within the other. If not, a cautious comparison of likelihoods can be informative. For an example, see Fit a Spatial Structure Model.
Description of the Fit Statistics Report uses the following notation:
• Specify the mixed model:

Here y is the nx1 vector of observations, β is a vector of fixed-effect parameters, γ is a vector of random-effect parameters, and ε is a vector of errors.
• The vectors γ and ε are assumed to have a multivariate normal distribution where
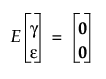
and
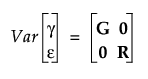
• With these assumptions, the variance of y is calculated as follows:
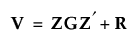
Description of the Fit Statistics Report
-2 Residual Log Likelihood
The final evaluation of twice the negative residual log-likelihood, the objective function.
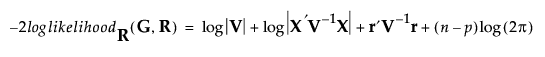
where

and p is the rank of X. Use the residual likelihood only for model comparisons where the fixed effects portion of the model is identical. See Likelihood, AICc, and BIC.
-2 Log Likelihood
The evaluation of twice the negative log-likelihood function. See Likelihood, AICc, and BIC.
Use the log-likelihood for model comparisons in which the fixed, random, and repeated effects differ in any of the models.
AICc
Corrected Akaike’s Information Criterion. See Likelihood, AICc, and BIC.
BIC
Bayesian Information Criterion. See Likelihood, AICc, and BIC.
 Convergence Score Test
Convergence Score Test
If there are problems with model convergence, a warning message is displayed below the fit statistics. Figure 8.11 shows the warning that suggests the cause and possible solutions to the convergence issue. It also includes a test of the relative gradient at the final iteration. If this test is non-significant, the model might be correct but not fully reaching the convergence criteria. In this case, consider using the model and results with caution. See Statistical Details for the Convergence Score Test.
Figure 8.11 Convergence Score Test
