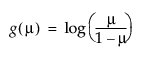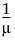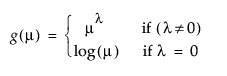Statistical Details for Generalized Linear Model Construction
To construct a generalized linear model, you must select response and explanatory variables for your data. You then must choose an appropriate link function and probability distribution for your response. Explanatory variables can be any combination of continuous variables, classification variables, and interactions. Some common examples of generalized linear models are listed in Table 13.1.
|
Model |
Response Variable |
Distribution |
Default Link Function |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Traditional Linear Model |
continuous |
Normal |
identity, g(μ) = μ |
|
Logistic Regression |
a count or a binary random variable |
Binomial |
logit, |
|
Poisson Regression in Log Linear Model |
a count |
Poisson |
log, g(μ) = log(μ) |
|
Exponential Regression |
positive continuous |
Exponential |
|
The platform fits a generalized linear model to the data by maximum likelihood estimation of the parameter vector. In general, there is no closed-form solution for the maximum likelihood estimates of the parameters. Therefore, the platform estimates the parameters of the model numerically through an iterative fitting process using a technique pioneered by Nelder and Wedderburn (1972). The overdispersion parameter φ is estimated by dividing the Pearson goodness-of-fit statistic by its degrees of freedom. Covariances, standard errors, and confidence limits are computed for the estimated parameters based on the asymptotic normality of maximum likelihood estimators.
A number of link functions and probability distributions are available in the Generalized Linear Model personality of the Fit Model platform. Table 13.2 lists the built-in link functions.
|
Link Function Name |
Link Function Formula |
|---|---|
|
Identity |
g(μ) = μ |
|
Logit |
|
|
Probit |
g(μ) = Φ-1(μ), where Φ is the standard normal cumulative distribution function |
|
Log |
g(μ) = log(μ) |
|
Reciprocal |
g(μ) = |
|
Power |
|
|
Comp LogLog |
g(m) = log(–log(1 – μ)) |
When you select the Power link function, a number box appears that enables you to enter the desired power.
Table 13.3 lists the variance functions associated with the available distributions for the response variable.
|
Distribution |
Variance Function |
|---|---|
|
Normal |
V(μ) = 1 |
|
Binomial |
V(μ) = μ(1 – μ) |
|
Poisson |
V(μ) = μ |
|
Exponential |
V(μ) = μ2 |