EMS (Traditional) Model Fit Reports
In the Fit Model launch window, if you select EMS as the fitting method, four new reports appear. The Effect Tests report is not shown, as tests for both fixed and random effects are conducted in the Tests wrt Random Effects report.
Caution: The use of EMS is not recommended. REML is the recommended method.
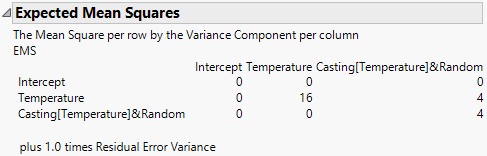
Expected Mean Squares
The expected mean square for a model effect is a linear combination of variance components and fixed effect values, including the residual error variance. This table gives the coefficients that define the expected mean square for each model effect. The rows of the matrix correspond to the effects, listed on the left. The columns correspond to the variance components, identified across the top. Each expected mean square includes the residual variance with a coefficient of one. This information is given beneath the table.
Figure 3.49 shows the Expected Mean Squares report for the Investment Castings.jmp sample data table. Run the Model - EMS script and then run the model.
Figure 3.49 Expected Mean Squares Report
As indicated by the table, the expected mean square for Casting[Temperature] is
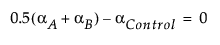
Variance Component Estimates
Estimates of the variance components are obtained by equating the expected mean squares to the corresponding observed mean squares and solving. The Variance Component Estimates report gives the estimated variance components.
Component
The random effects.
Var Comp Est
The estimate of the variance component.
Percent of Total
The ratio of the variance component to the sum of the variance components.
CV
The coefficient of variation for the variance component. It is 100 times the square root of the variance component, divided by the mean response.
Note: Appears only if you right-click in the report and select Columns > CV.
Test Denominator Synthesis
For each effect to be tested, an F statistic is constructed. The denominator for this statistic is the mean square whose expectation is that of the numerator mean square under the null hypothesis. This denominator is constructed, or synthesized, from variance components and values associated with fixed effects.
Source
The effect to be tested.
MS Den
The estimated mean square for the denominator of the F test.
DF Den
The degrees of freedom for the synthesized denominator. These are constructed using Satterthwaite’s method (Satterthwaite 1946).
Denom MS Synthesis
The variance components used in the denominator synthesis. The residual error variance is always part of this synthesis.
Tests wrt Random Effects
Tests for fixed and random effects are presented in this report.
Source
The effects to be tested. These include fixed and random effects.
SS
The sum of squares for the effect.
MS Num
The numerator mean square.
DF Num
The numerator degrees of freedom.
F Ratio
The F ratio for the test. It is the ratio of the numerator mean square to the denominator mean square. The denominator mean square can be obtained from the Test Denominator Synthesis report.
Prob > F
The p-value for the effect test.
Caution: Standard errors for least squares means and denominators for contrast F tests use the synthesized denominator. In certain situations, such as tests involving crossed effects compared at common levels, these tests might not be appropriate. Custom tests are conducted using residual error, and leverage plots are constructed using the residual error, so these also might not be appropriate.
EMS Profiler
When you use the EMS method and select Factor Profiling > Profiler, the profiler gives predictions and conditional mean confidence intervals based on the fixed-effects model. These values are not based on the predicted values for the random effects.