Connect to a Database With Open Table
JMP can communicate with databases using ODBC data sources using an ODBC manager. The ODBC manager and associated drivers depend on your operating system. After you create the data source in the operating system software, follow these steps to connect to the database in JMP.
1. Select File > Database > Open Table. The Connections box lists data sources that you have connected to in the current JMP session.
2. Click New Connection.
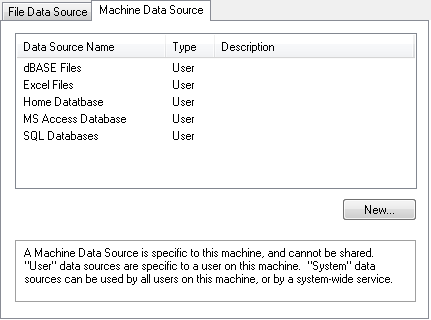
3. (Windows) In the Select Data Source window (Figure 3.54), click the Machine Data Source tab, select the data source, click OK, enter the user name and password, and then click OK.
(macOS) In the Choose DSN window, select the data source, enter the user name and password, and then click Choose DSN.
Figure 3.54 Select a Data Source (Windows)
The new connection is shown in the Database Open Table window.
Open Data from a Database
After you connect to the ODBC database and select a table to import, the data is opened in a data table. Several table scripts are included in the data table.
• Run the Source script to reconnect to the database.
• Run the Update from DB script to re-import and refresh the data. If the database table has the same number of columns as the original JMP table, the values in that existing JMP table are updated in place. However, if the number of columns is not the same, then a new data table opens where the updated data is stored.
• Run the Save to DB script to save the data table to the database. The existing data in the database is replaced. This script might contain the user name and password. The preference called Hide ODBC Connection Strings can be set to prevent including this possibly sensitive information. Select File > Preferences > Tables (Windows) to find the preference (or JMP > Preferences > Tables on macOS).
To import data from a database
1. Select File > Database > Open Table.
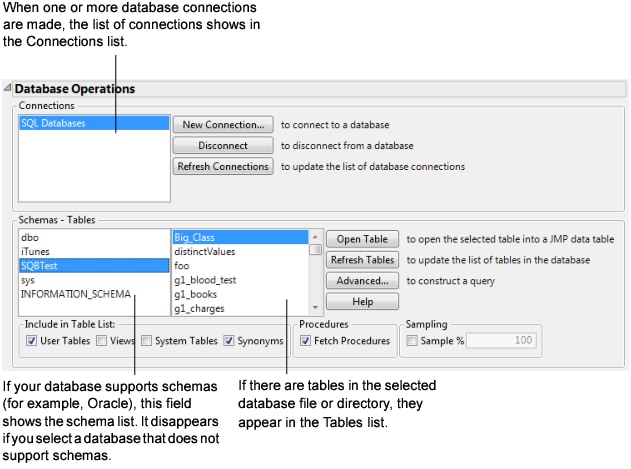
The Database Open Table window appears (Figure 3.55).
2. If you are already connected to the database, select it in the Connections box. Follow the steps in Connect to a Database With Open Table.
The Connections box lists data sources to which JMP is connected. The Schemas - Tables box lists schemas for those databases that support them.
Figure 3.55 Database Open Table Window
Note: The Fetch Procedures check box is disabled if the ODBC driver does not support fetching procedures.
3. If the desired data source is not listed in the Connections box, click New Connection to choose a data source. The method of choosing a data source depends on your operating system.
4. Select the desired data source in the Connections box. The tables list in the Tables box updates accordingly. The update might take a several seconds, depending on the number of tables and the speed of the connection to the database. If your database supports schemas, tables are loaded for the first schema in the list, and on other schemas as you click them.
5. Control which tables are listed by choosing the options in the Include in Table List group of check boxes.
Note: Different drivers interpret these labels differently.
User Tables When clicked, displays all available user tables in the Tables list. User tables are specific to which user is logged on to the computer.
Views When clicked, displays “views” in the Tables list along with all other file types that can be opened. “Views” are virtual tables that are query result sets updated each time you open them. They are used to extract and combine information from one or more tables.
System Tables When clicked, displays all available system tables in the Tables list. System tables are tables that can be used by all users or by a system-wide service.
Synonyms When clicked, displays all available ORACLE synonyms in the Tables list.
Sampling Enter the percentage of rows that you want to appear in the list of tables. Selecting this option speeds up queries in large databases. JMP uses the sampling method supported by the database. The check box is unavailable when the database does not support sampling.
6. Select the desired table from the Tables list.
Note: If you are connected to a dBase database, select the database folder to which you would like to connect. Individual files are grayed out and cannot be selected.
7. Click Open Table to import all the data in the selected table, or click Advanced to specify a subset of the table to be imported. Some databases require that you enter the user ID and password to access the data.
You might see a short delay when opening large tables. To see the status of all active ODBC queries, select View > Running Queries.
Note: If the data were previously exported to a database in JMP and contained an Expression column, the column will be imported as a Character column. Select Cols > Column Info and change the Data Type to Expression.
Write SQL Statements to Query a Database
You can use Structured Query Language (SQL) statements to control what you import from a database. When you open a database file in JMP, you are actually sending a SQL statement to the database. By default, this statement gets all columns and records in the database table. In some cases, this is too much data. When you are interested only in a subset of the table’s data, you can customize the SQL request to only request the data that you want. After you execute a SQL query, the code for the query is stored in the data table in the SQL table variable.
This section describes how to write SQL statements to retrieve data. To interactively query data without writing SQL statements, use Query Builder. You can also start creating a query in Query Builder and then add your own SQL. See Write SQL Statements in Query Builder.
1. Select File > Database > Open Table.
The Database Open Table window appears (Figure 3.55).
2. Connect to the database if necessary or select an existing database connection. Follow the steps in Connect to a Database With Open Table.
The Connections box lists data sources to which JMP is connected. The Schemas - Tables box lists schemas for those databases that support them.
Note: The SQL Query that you run in this window operates only on the tables and procedures that are displayed in the left panes of the window. Running unrelated SQL here has no results.
3. From the Database Open Table window, click the Advanced button to open specific subsets of a table.
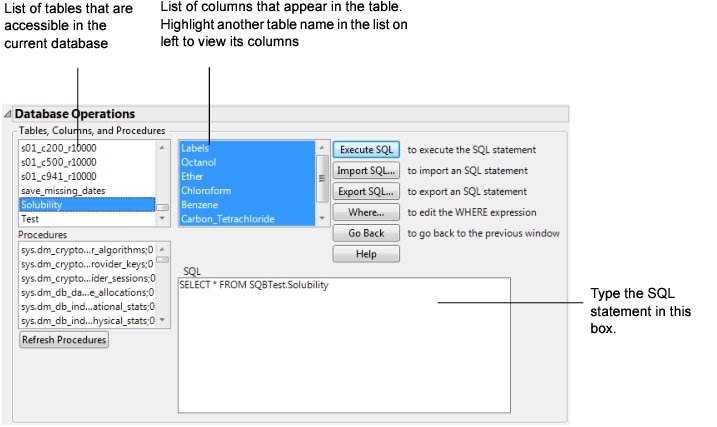
4. Either type in a valid SQL statement, or modify the default statement. Figure 3.56 shows a default SQL Select statement appropriate for the selected file. See Structured Query Language (SQL): A Reference, for a description of SQL statements that you can use.
Instead, you can add expressions by clicking the Where button and using the WHERE Clause editor to create expressions. See Use the WHERE Clause Editor.
Figure 3.56 Reading All Variables from the Solubility Table Stored in an Excel File
5. Click Execute SQL. A JMP data table appears with the columns that you selected. See Use Data Table Variables.
6. To see the status of all running queries, select View > Running Queries.
Note that you can enter any valid SQL statement and click Execute SQL to execute the command. Valid SQL varies with the data source and ODBC driver.