Optimality Criterion for Accelerated Life Tests
Consider an accelerated life test (ALT) to be conducted across at most three acceleration factors xi with Ji levels, respectively. The goal of test planning is to determine the number of samples to allocate to each combination of the factor levels.
The computation of the optimality criterion depends on the overall Fisher information matrix from the individual level-specific information matrices
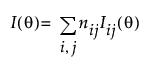
as well as the inclusion of prior uncertainty S where appropriate.
Quantile Optimality
The quantile optimal design Dq is the design that minimizes the expression:
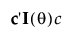
where the vector c depends on the lowest use condition.
For the single use condition
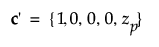
where zp is the pth quantile of the failure distribution.
Failure Probability Optimality
The failure probability optimal design Df is the design that minimizes the expression:
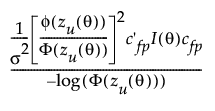
where zU(θ) is the standardized log-time at use conditions as defined in Quantile Optimality. cfp is similar to c as defined in Quantile Optimality except that the last entry is zU(θ). The quantity in the numerator is based on the asymptotic variance of logΦ(zU(θ)), where the log-transformation is used for numerical stability.