Statistical Details for Variance Components
The exact model type that you choose in the Variability Chart platform depends on how the data were collected. For example, if the operators are measuring the same parts, you have a crossed design. If they measuring different parts, you have a nested design. To illustrate, in a model where B is nested within A, multiple measurements are nested within both B and A, and there are na•nb•nw measurements, the following statements hold:
• na random effects are due to A
• na•nb random effects due to each nb B levels within A
• na•nb•nw random effects due to each nw levels within B within A:
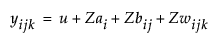 .
.
The Zs are the random effects for each level of the classification. Each Z is assumed to have a mean of zero and to be independent from all other random terms. The variance of the response y is the sum of the variances due to each z component:
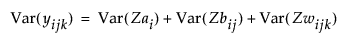 .
.
Table 6.3 shows the supported models and what the effects in the model would be.
|
Model |
Factors |
Effects in the Model |
|---|---|---|
|
Main Effects |
1 2 unlimited |
A A, B and so on, for more factors |
|
Crossed |
1 2 3 4 unlimited |
A A, B, A*B A, B, A*B, C, A*C, B*C, A*B*C A, B, A*B, C, A*C, B*C, A*B*C, D, A*D, B*D, A*B*D, C*D, A*C*D, B*C*D, A*B*C*D, and so on, for more factors |
|
Nested |
1 2 3 4 unlimited |
A A, B(A) A, B(A), C(A,B) A, B(A), C(A,B), D(A,B,C) and so on, for more factors |
|
Crossed then Nested |
3 |
A, B, A*B, C(A,B) |
|
Nested then Crossed |
3 |
A, B(A), C, A*C, C*B(A) |