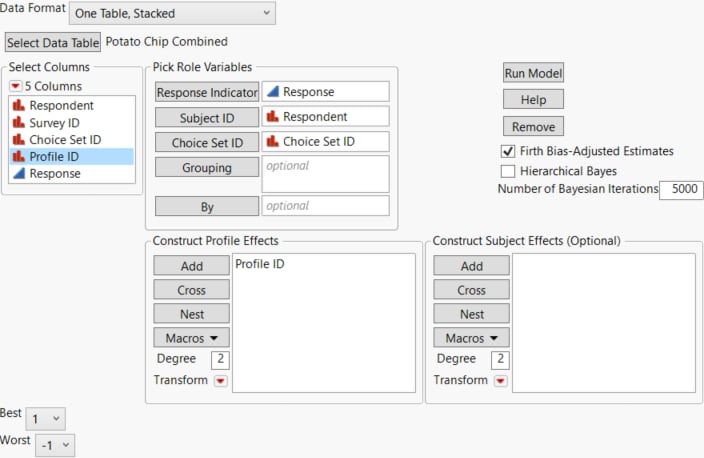
Launch Window for One Table, Stacked
Launch the MaxDiff platform by selecting Analyze > Consumer Research > MaxDiff. If your MaxDiff data is in a single table, select One Table, Stacked from the Data Format menu.
Figure 5.9 Launch Window for One Table, Stacked Data Format
For more information about the options in the Select Columns red triangle menu, see “Column Filter Menu” in Using JMP.
Select Data Table
Select or open the data table that contains the combined data. Select Other to open a file that is not already open.
Response Indicator
A column containing the preference data. Use two of the values 1, -1, or 0 for the Best and Worst choices, and the third value for profiles that are not Best or Worst. The default coding is a 1 to indicate the Best choice and a -1 for the Worst choice.
Subject ID
An identifier for the study participant.
Choice Set ID
An identifier for the set of profiles presented to the subject for a given preference determination.
Grouping
A column which, when used with the Choice Set ID, uniquely designates each choice set. For example, if a choice set has Choice Set ID = 1 for Survey = A, and another choice set has Choice Set ID = 1 for Survey = B, then Survey should be used as a Grouping column.
By
Produces a separate report for each level of the By variable. If more than one By variable is assigned, a separate report is produced for each possible combination of By variables.
Construct Profile Effects
Add effects constructed from the attributes for the profiles.
For information about the Construct Profile Effects panel, see “Construct Model Effects” in Fitting Linear Models.
Construct Subject Effects (Optional)
Add effects constructed from subject-related factors.
For information about the Construct Subject Effects panel, see “Construct Model Effects” in Fitting Linear Models.
Firth Bias-adjusted Estimates
Computes bias-corrected MLEs that produce better estimates and tests than MLEs without bias correction. These estimates also improve separation problems that tend to occur in logistic-type models. See Heinze and Schemper (2002) for a discussion of the separation problem in logistic regression.
 Hierarchical Bayes
Hierarchical Bayes
Uses a Bayesian approach to estimate subject-specific parameters. See Bayesian Parameter Estimates.
 Number of Bayesian Iterations
Number of Bayesian Iterations
(Applicable only if Hierarchical Bayes is selected.) The total number of iterations of the adaptive Bayes algorithm used to estimate subject effects. This number includes a burn-in period of iterations that are discarded. The number of burn-in iterations is equal to half of the Number of Bayesian Iterations specified on the launch window.